Small Internet Protocol Stack using a standard serial port.
PPP-Blinky - TCP/IP Networking Over a Serial Port
Note: The source code is at the bottom of this page.
A Windows desktop showing PPP-Blinky in the network connections list.
Describe PPP-Blinky in Three Sentences
PPP-Blinky is a tiny library that enables Internet protocols (IPv4) to any mbed target hardware by using only a serial port.
The code runs on processors with as little as 8k RAM, for example the Nucleo-L053R8 board.
PPP-Blinky uses the industry-standard PPP (Point-to-Point) Protocol and a tiny "stateless" TCP/IP stack.
No Ethernet Port Required
No ethernet port is required - PPP-Blinky uses a serial port to send IP packets to your PC.
PPP-Blinky emulates a standard dial-up modem and therefore connects to Windows, Linux or Adroid machines.
The code runs on most ARM mbed platforms such as the LPC11U24 shown in the picture below:
 mbed LPC11u24 acting as a webserver to a Windows laptop.
mbed LPC11u24 acting as a webserver to a Windows laptop.
Webserver
The Webserver and WebSocket functions are ideal for building browser-based GUIs on mbed-enabled hardware.
PPP-Blinky's HTTP webserver works with most web clients such as Internet Explorer, Mozilla Firefox, Google Chrome, Safari, Curl, wget and Lynx as well as Microsoft Powershell Invoke-Webrequest command.
In the image below Firefox web browser displays the main web page embedded into PPP-Blinky's code:
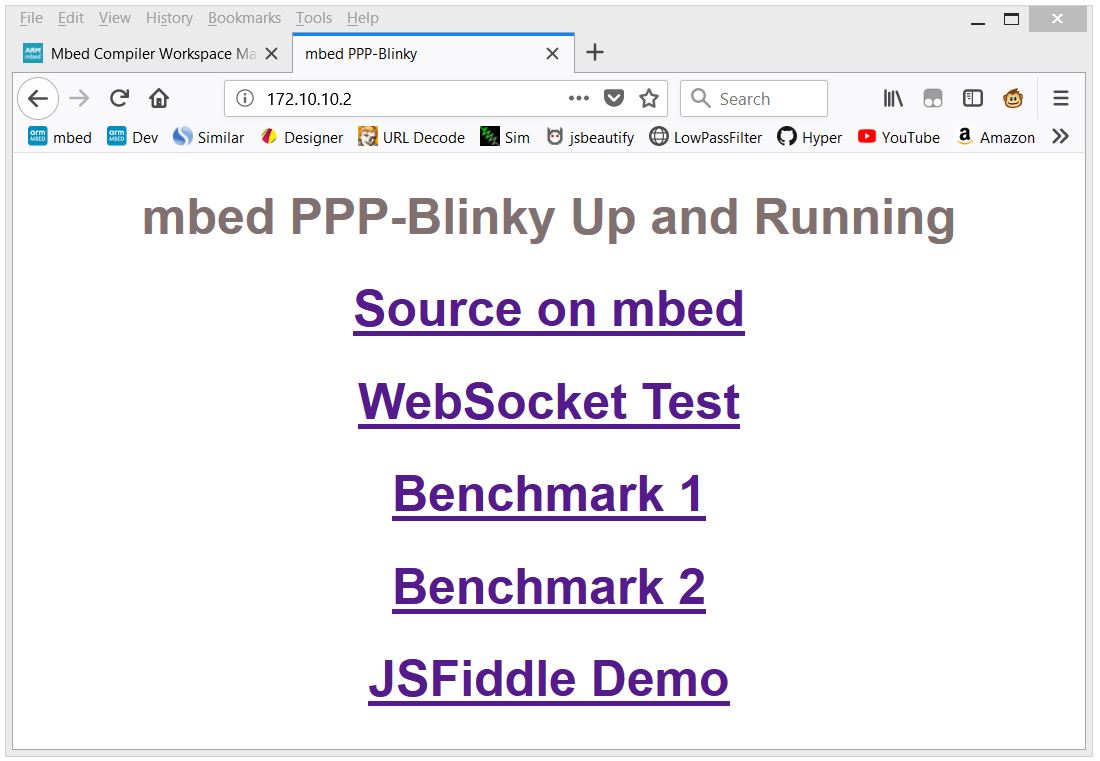 Firefox web browser displays a web page embedded into PPP-Blinky's code
Firefox web browser displays a web page embedded into PPP-Blinky's code
WebSocket Service
WebSocket is the most popular protocol standard for real-time bidirectional TCP/IP communication between clients and servers.
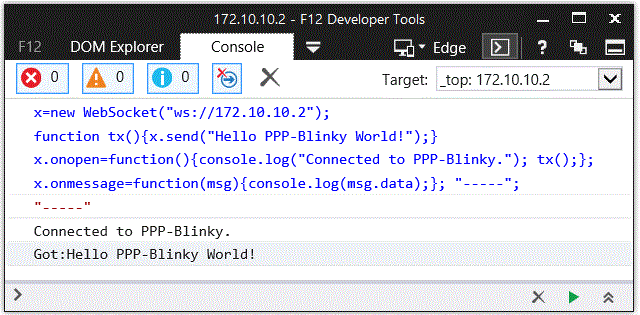
In the image below a small Internet Explorer script has connected to PPP-Blinky's WebSocket Service.
A websocket message was then sent by the browser and was echoed back by the WebSocket, triggering the onmessage event in the script.
The WebSocket service enables bidirectional real-time interaction between PPP-Blinky and any element in the browser DOM via JavaScript.
If you already have PPP-Blinky up and running you can test your WebSocket service using this: http://jsfiddle.net/d26cyuh2/112/embedded/result
Websockets are ideal for building browser-based GUIs for mbed hardware.
Trying PPP-Blinky on your mbed board
You will need an mbed-enabled hardware board: https://developer.mbed.org/platforms/
Establish a serial port connection between your host PC and your mbed board.
The easiest way is to use mbed hardware with a USB serial debug port. I've tried the ST-Micro Nucleo-L476RG, Nucleo-L152RE, Nucleo-F401RE, Nucleo-L432KC, Nucleo-L053R8, mbed-LPC11U24 and mbed-LPC1768 boards and they all work out of the box. Use the mbed online compiler to compile the software for your target board. Save the compiled binary to your hardware.
Before establishing a network connection, you can verify the operation of the code by opening a terminal program such as Tera Term, and setting the baud rate of the COM port on your mbed board to 115200 baud. LED1 should toggle for every two 0x7E (~) (i.e. tilde) characters you type, as 0x7E is the PPP frame start/end marker. Don't forget to close the port when your'e done testing, or else Windows Dial-up Networking will report that the COM port is in use by another program when you try to connect.
Once you are certain that the serial port and firmware is working, proceed to creating a new network connection on your PC -see below.
Creating a Dial-up Connection in Windows
Setting up Dial-Up Networking (DUN) on your Windows 7 or 8 PC is essentially a two-step process: First, you create a new modem device, because PPP-blinky partially emulates a standard Windows serial port modem device. Second, you create a new Internet connection (in practice, a new network adapter) which is associated with your new "modem".
Step-by-step description of how to configure Windows for PPP-Blinky here:
/users/nixnax/code/PPP-Blinky/wiki/Configuring-Windows-Dial-Up-Networking
There is also a screen on how to set up Linux dial-up networking near the bottom of this page.
Connecting to PPP-Blinky from your PC
Once Windows networking is configured you can establish a dial-up connection to your mbed board over the USB virtual com port.
The IP address you manually assigned to the new dial-up network adapter (172.10.10.1) functions as a gateway to any valid IP address on that subnet. In the screen capture below, I'm sending pings from the Windows 8 command line to my ST-Micro Nucleo-L476RG board over the USB virtual serial Port. I'm also using a second serial port and Tera Term to capture the debug output from a second serial port on the hardware. The optional debug output from the board prints out the IP source and destination address and the first few bytes of the data payload. Note that the source is the adapter IP address, (172.10.10.1 in this case) and the destination is some other address on that subnet - all packets to the subnet are sent to our mbed hardware. For example, you could also ping 172.10.10.123 or, if your PPP-Blinky is running, simply click on this link: http://172.10.10.123
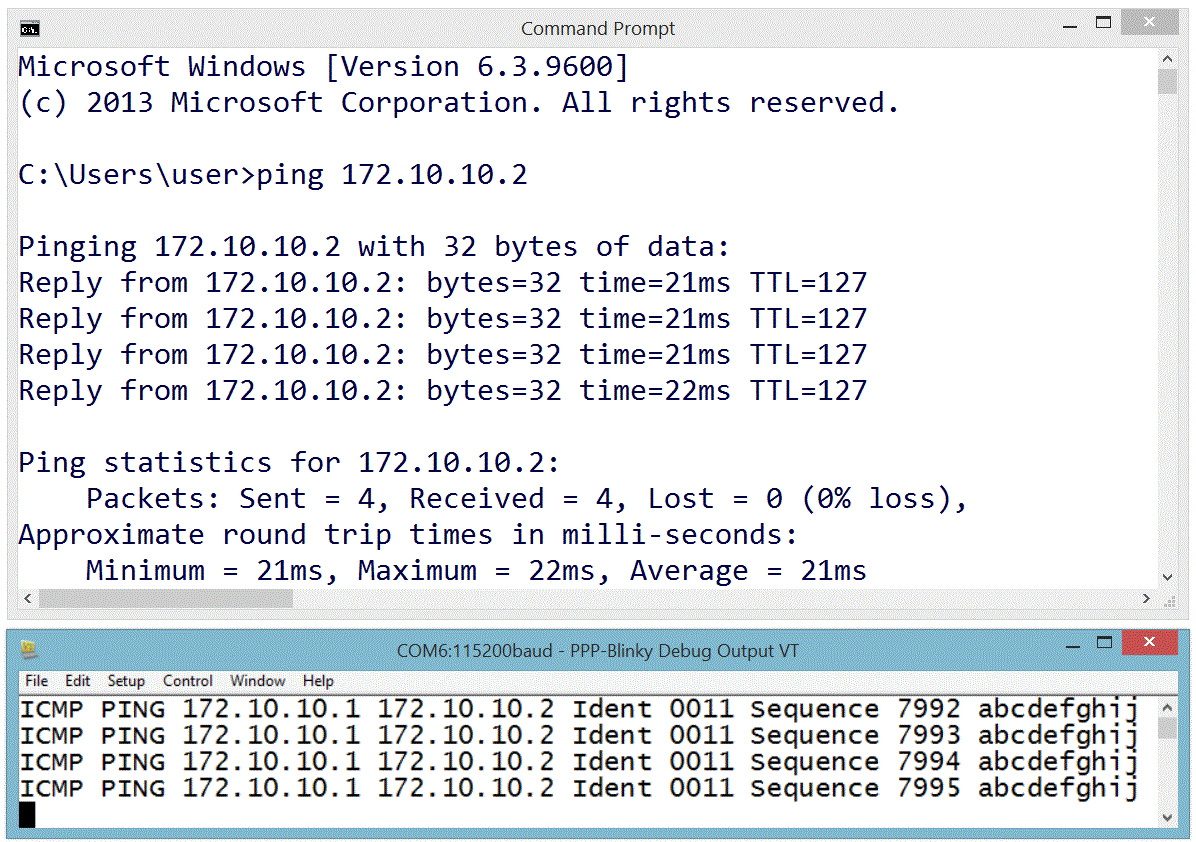
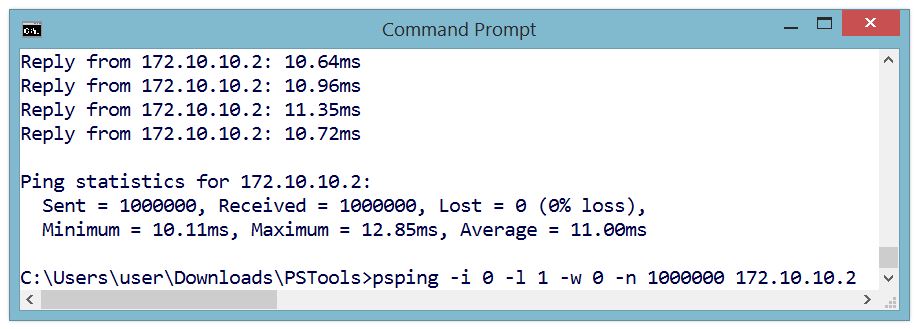
One Million Pings!
In the image below the ICMP ("ping") echo reply service was tested by sending one million pings to ppp-Blinky. This took over two hours.
The ping tool used on the Windows 8 PC was psping.exe from PsTools by Mark Russinovich - http://bit.ly/PingFast
The average reply time for a short ping (1 byte of payload data) was 11 milliseconds at 115200 baud on the $10 Nucleo-L053R8 board - barely enough time for 130 bytes to be sent over the port!
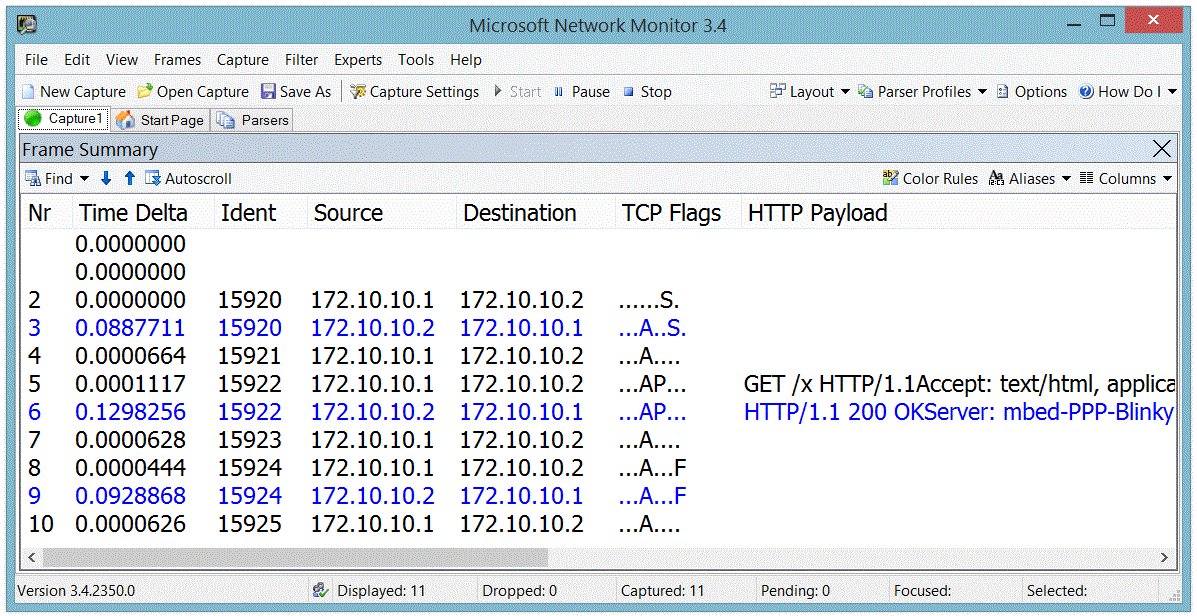
Monitoring PPP-Blinky Packets
The image below is from a Microsoft Network Monitor 3.4 capture session.
Responses from PPP-Blinky are shown in blue.
Frame 2 - Internet Explorer at IP 172.10.10.1 (the Dial-Up Adapter IP) requests a TCP connection by sending an S (SYN) flag.
Frame 3 - PPP-Blinky at IP 172.10.10.2 responds with an ACK in frame 3. One direction of the link is now established.
Frame 4 - The PC acknowledges the SYN sent by PPP-Blinky in frame 3. The TCP link is now fully established.
Frame 5 - The browser "pushes" (P flag is set) an HTTP GET request to PPP-Blinky.
Frame 6 - PPP-Blinky responds with a standard HTTP response "pushes" (P flag set) back a small web page. It also sets the A (ACK) flag to acknowledge the message sent in frame 6.
Frame 7 - The PC acknowledges reception of the HTTP payload.
Frame 8 - The PC starts to shut down the TCP connection by sending a FIN flag.
Frame 9 - PPP-Blinky acknowledges the FIN request - the connection is now closed in one direction. It also sets a FIN flag in the response to request closure of the opposite direction of the connection.
Frame 10 - The PC acknowledges the FIN request. The closing of the TCP connection is now confirmed in both directions.
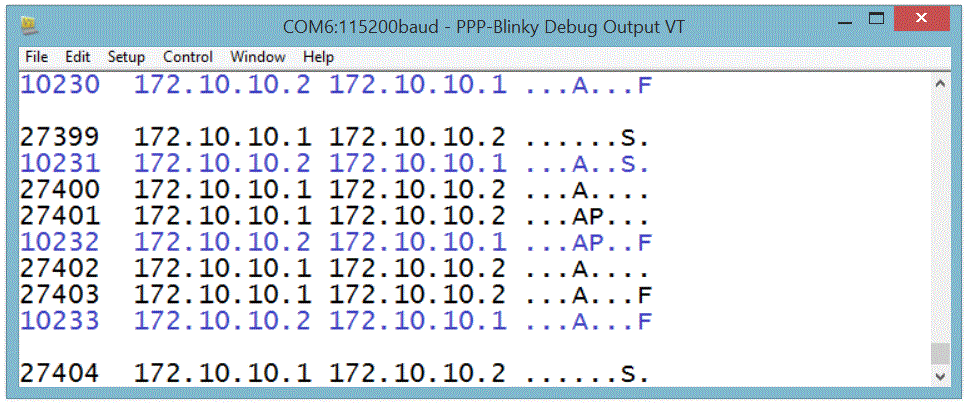
Debug Output
PPP-Blinky can output handy debug information to an optional second serial port.
The image below shows the debug output (Ident, Source, Destination, TCP Flags) for a complete HTTP conversation.
The PC messages are displayed in black. PPP-Blinky messages are blue.
Notice how PPP-blinky automatically inserts a blank line after each full HTTP conversation.
Creating a Dial-Up Connection in Linux
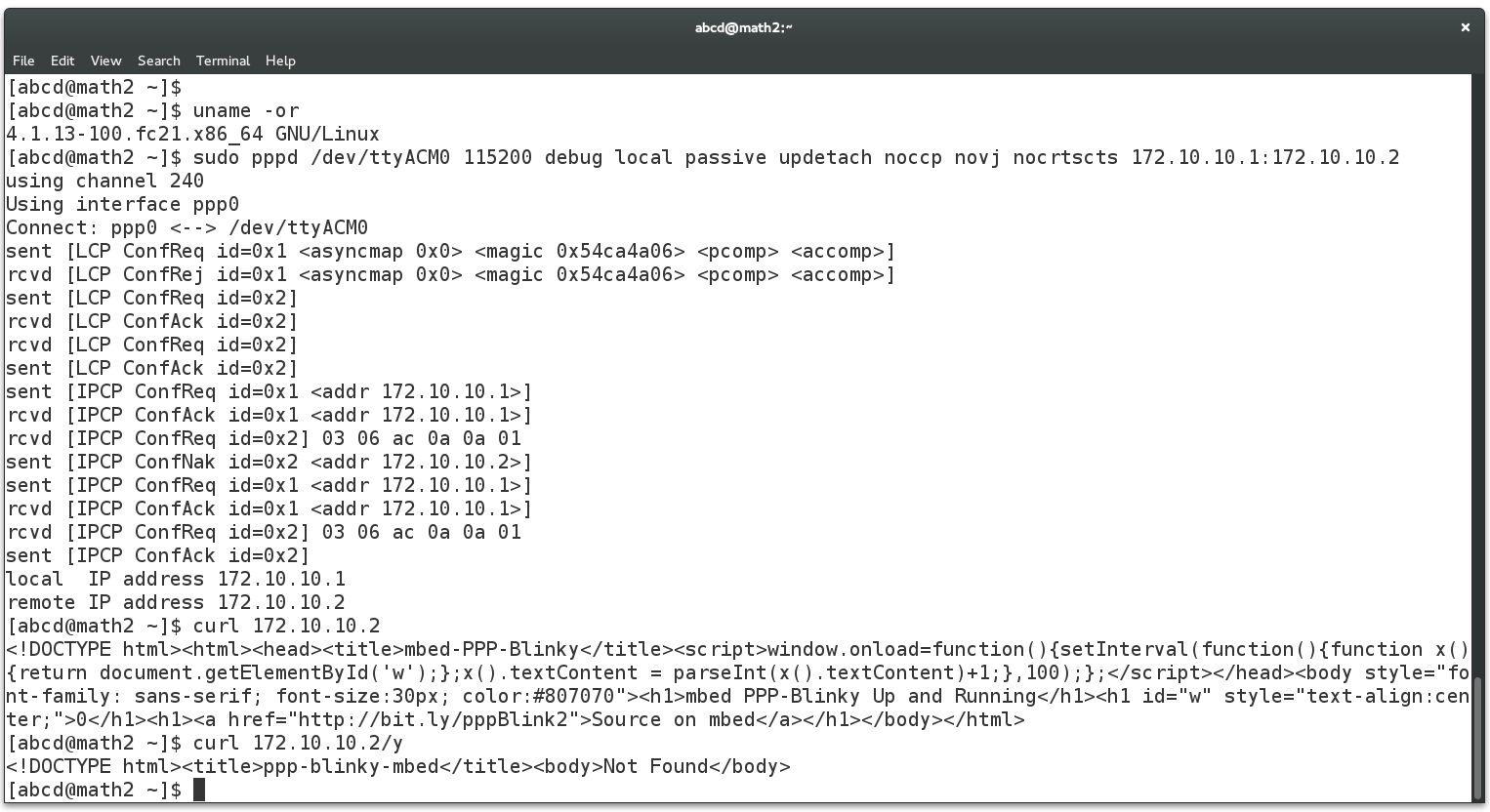
The screen below shows the required pppd command to connect to PPP-Blinky from a Linux machine. This was much simpler than Windows! The USB serial port of the mbed LPC1768 board registered as /dev/ttyACM0 on my Linux box. Do a websearch on pppd if you want to learn more about pppd, the Linux PPP handler. Near the bottom of the screen below, two webpages are fetched (/ and /y) by using the curl command on the command line. Gnome Webkit and Firefox work fine, too. Also try echo GET / HTTP/1.1 | nc 172.10.10.2 which uses netcat, the "Swiss army knife" of networking tools. PPP-Blinky was also tested with ApacheBench, the Apache server benchmark software. After 100000 fetches, the mean page fetch rate was reported as 6 page fetches per second for a small page.
Caveats
PPP Blinky is an extremely sparse implementation (1.5k lines) of HTTP,WebSocket,TCP, UDP, ICMP, IPCP and LCP over PPP, requiring around 8kB of RAM. The minimum functionality required to establish connectivity is implemented. These are often acceptable tradeoffs for embedded projects as well as a handy tool to learn the practical details of everyday networking implementations.
PPP-Blinky/ppp-blinky.cpp@143:c5019f856a56, 2017-08-29 (annotated)
- Committer:
- nixnax
- Date:
- Tue Aug 29 17:26:42 2017 +0000
- Revision:
- 143:c5019f856a56
- Parent:
- 142:54d1543e23e5
- Child:
- 144:01d98cf7738e
Register Adapter IP in IPCP. Comments.
Who changed what in which revision?
| User | Revision | Line number | New contents of line |
|---|---|---|---|
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 1 | // PPP-Blinky - "The Most Basic Internet Of a Thing" |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 2 | // A Tiny HTTP Webserver Using Windows XP/7/8/10/Linux Dial-Up Networking Over A Serial Port. |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 3 | // Receives UDP packets and responds to ping (ICMP Echo requests) |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 4 | // WebSocket Service - see https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/WebSocket |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 5 | |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 6 | // Copyright 2016/2017 Nicolas Nackel aka Nixnax. Permission is hereby granted, free of charge, to any person obtaining a copy of this software and associated documentation files (the "Software"), to deal in the Software without restriction, including without limitation the rights to use, copy, modify, merge, publish, distribute, sublicense, and/or sell copies of the Software, and to permit persons to whom the Software is furnished to do so, subject to the following conditions: The above copyright notice and this permission notice shall be included in all copies or substantial portions of the Software. THE SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED "AS IS", WITHOUT WARRANTY OF ANY KIND, EXPRESS OR IMPLIED, INCLUDING BUT NOT LIMITED TO THE WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY, FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE AND NONINFRINGEMENT. IN NO EVENT SHALL THE AUTHORS OR COPYRIGHT HOLDERS BE LIABLE FOR ANY CLAIM, DAMAGES OR OTHER LIABILITY, WHETHER IN AN ACTION OF CONTRACT, TORT OR OTHERWISE, ARISING FROM, OUT OF OR IN CONNECTION WITH THE SOFTWARE OR THE USE OR OTHER DEALINGS IN THE SOFTWARE. |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 7 | |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 8 | // Notes and Instructions |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 9 | // http://bit.ly/PPP-Blinky-Instructions |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 10 | // http://bit.ly/win-rasdial-config |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 11 | |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 12 | // Handy reading material |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 13 | // https://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/cc957992.aspx |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 14 | // https://en.wikibooks.org/wiki/Serial_Programming/IP_Over_Serial_Connections |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 15 | // http://atari.kensclassics.org/wcomlog.htm |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 16 | |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 17 | // Handy tools |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 18 | // https://ttssh2.osdn.jp/index.html.en - Tera Term, a good terminal program to monitor the debug output from the second serial port with! |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 19 | // https://www.microsoft.com/en-us/download/details.aspx?id=4865 - Microsoft network monitor - real-time monitoring of PPP packets |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 20 | // http://pingtester.net/ - nice tool for high rate ping testing |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 21 | // http://www.sunshine2k.de/coding/javascript/crc/crc_js.html - Correctly calculates the 16-bit FCS (crc) on our frames (Choose CRC16_CCITT_FALSE), then custom relected-in=1, reflected-out=1 |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 22 | // https://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/sysinternals/pstools.aspx - psping for fast testing of ICMP ping function |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 23 | // https://eternallybored.org/misc/netcat/ - use netcat -u 172.10.10.1 80 to send/receive UDP packets from PPP-Blinky |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 24 | // Windows Powershell invoke-webrequest command - use it to stress test the webserver like this: while (1){ invoke-webrequest -uri 172.10.10.1/x } |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 25 | |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 26 | // Connecting PPP-Blinky to Linux |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 27 | // PPP-Blinky can be made to talk to Linux - tested on Fedora - the following command, which uses pppd, works: |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 28 | // pppd /dev/ttyACM0 115200 debug dump local passive noccp novj nodetach nocrtscts 172.10.10.1:172.10.10.2 |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 29 | // in the above command 172.10.10.1 is the adapter IP, and 172.10.10.2 is the IP of PPP-Blinky. |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 30 | // See also https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Point-to-Point_Protocol_daemon |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 31 | |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 32 | // Special pages when PPP-Blinky is running |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 33 | // 172.10.10.2 root page |
| nixnax | 143:c5019f856a56 | 34 | // 172.10.10.2/x returns a number that increments every time you request a page - this is handy for testing |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 35 | // 172.10.10.2/xb also returns a number, but issues a fast refresh command. This allows you to use your browser to benchmark page load speed |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 36 | // 172.10.10.2/ws a simple WebSocket demo |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 37 | // http://jsfiddle.net/d26cyuh2/ more complete WebSocket demo in JSFiddle |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 38 | |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 39 | // Ok, enough talking, time to check out some code!! |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 40 | |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 41 | #include "ppp-blinky.h" |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 42 | |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 43 | // The #define below enables/disables a second (OPTIONAL) serial port that prints out interesting diagnostic messages. |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 44 | // Change to SERIAL_PORT_MONITOR_YES to enable diagnostics messages. You need to wire a second serial port to your mbed hardware to monitor this. |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 45 | // Using the second serial port will slow down packet response time |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 46 | // Note - the LPC11U24 does NOT have a second serial port |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 47 | #define SERIAL_PORT_MONITOR_NO /* change to SERIAL_PORT_MONITOR_YES for debug messages */ |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 48 | |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 49 | // here we define the OPTIONAL, second debug serial port for various mbed target boards |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 50 | #ifdef SERIAL_PORT_MONITOR_YES |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 51 | #if defined(TARGET_LPC1768) |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 52 | Serial xx(p9, p10); // Second serial port on LPC1768 - not required to run, if you get compile error here, change #define SERIAL_PORT_MONITOR_YES to #define SERIAL_PORT_MONITOR_NO |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 53 | #elif defined(TARGET_NUCLEO_F446RE) || defined(TARGET_NUCLEO_L152RE) || defined(TARGET_NUCLEO_L053R8) || defined(TARGET_NUCLEO_L476RG) || defined(TARGET_NUCLEO_F401RE) |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 54 | Serial xx(PC_10, PC_11); // Second serial port on NUCLEO boards - not required to run, if you get compile error here, change #define SERIAL_PORT_MONITOR_YES to #define SERIAL_PORT_MONITOR_NO |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 55 | #elif defined(TARGET_LPC11U24) |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 56 | #error The LPC11U24 does not have a second serial port to use for debugging - change SERIAL_PORT_MONITOR_YES back to SERIAL_PORT_MONITOR_NO |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 57 | #elif defined (TARGET_KL46Z) || (TARGET_KL25Z) |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 58 | Serial xx(PTE0,PTE1); // Second serial port on FRDM-KL46Z board |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 59 | #elif defined(YOUR_TARGET_BOARD_NAME_HERE) |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 60 | // change the next line to YOUR target board's second serial port pin definition if it's not present - and if it works, please send it to me - thanks!!! |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 61 | Serial xx(p9, p10); // change this to YOUR board second serial port pin definition - and please send it to me if it works!!! |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 62 | #else |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 63 | #error Add your target board's second serial port here if you want to use debugging - or simply change SERIAL_PORT_MONITOR_YES to SERIAL_PORT_MONITOR_NO |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 64 | #endif |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 65 | #define debugPrintf(x...) xx.printf (x) /* if we have a serial port we print debug messages */ |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 66 | #define debugPutc(x...) xx.putc(x) |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 67 | #define debugBaudRate(x...) xx.baud(x) |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 68 | #else |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 69 | // if we don't have a debug port the debug print functions do nothing |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 70 | #define debugPrintf(x...) {} |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 71 | #define debugPutc(x...) {} |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 72 | #define debugBaudRate(x...) {} |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 73 | #endif |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 74 | |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 75 | // verbosity flags used in debug printouts - change to 1 to see increasingly more detailed debug info. |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 76 | #define v0 1 |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 77 | #define v1 0 |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 78 | #define v2 0 |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 79 | #define IP_HEADER_DUMP_YES /* YES for ip header dump */ |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 80 | #define TCP_HEADER_DUMP_YES /* YES for tcp header dump */ |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 81 | |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 82 | // this is the webpage we serve when we get an HTTP request to root (/) |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 83 | // keep size under ~900 bytes to fit into a single PPP packet |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 84 | |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 85 | const static char rootWebPage[] = "\ |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 86 | <!DOCTYPE html>\ |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 87 | <html>\ |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 88 | <head>\ |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 89 | <title>mbed PPP-Blinky</title>\ |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 90 | <script>\ |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 91 | window.onload=function(){\ |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 92 | setInterval(function(){function x(){return document.getElementById('w');};\ |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 93 | x().textContent=parseInt(x().textContent)+1;},100);};\ |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 94 | </script>\ |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 95 | </head>\ |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 96 | <body style=\"font-family: sans-serif; font-size:20px; text-align:center; color:#807070\">\ |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 97 | <h1>mbed PPP-Blinky Up and Running</h1>\ |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 98 | <h1 id=\"w\">0</h1>\ |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 99 | <h1><a href=\"http://bit.ly/pppBlink2\">Source on mbed</a></h1>\ |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 100 | <h1><a href=\"/ws\">WebSocket Demo</a></h1>\ |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 101 | <h1><a href=\"/x\">Benchmark 1</a></h1>\ |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 102 | <h1><a href=\"/xb\">Benchmark 2</a></h1>\ |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 103 | <h1><a href=\"http://jsfiddle.net/d26cyuh2/\">JSFiddle Demo</a></h1>\ |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 104 | </body>\ |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 105 | </html>"; // size = 634 bytes plus 1 null byte = 635 bytes |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 106 | |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 107 | const static char webSocketPage[] = "\ |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 108 | <!DOCTYPE html>\ |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 109 | <html>\ |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 110 | <head>\ |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 111 | <title>mbed PPP-Blinky</title>\ |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 112 | <script>\ |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 113 | window.onload=function(){\ |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 114 | var url=\"ws://172.10.10.2\";\ |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 115 | var sts=document.getElementById(\"sts\");\ |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 116 | var btn=document.getElementById(\"btn\");\ |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 117 | var ctr=0;\ |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 118 | function show(text){sts.textContent=text;}\ |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 119 | btn.onclick=function(){\ |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 120 | if(btn.textContent==\"Connect\"){\ |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 121 | x=new WebSocket(url);\ |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 122 | x.onopen=function(){\ |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 123 | show(\"Connected to : \"+url);\ |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 124 | btn.textContent=\"Send \\\"\"+ctr+\"\\\"\";\ |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 125 | };\ |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 126 | x.onclose=function(){show(\"closed\");};\ |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 127 | x.onmessage=function(msg){show(\"PPP-Blinky Sent: \\\"\"+msg.data+\"\\\"\");};\ |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 128 | } else {\ |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 129 | x.send(ctr);\ |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 130 | ctr=ctr+1;\ |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 131 | btn.textContent=\"Send \\\"\"+ctr+\"\\\"\";\ |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 132 | }\ |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 133 | };\ |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 134 | };\ |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 135 | </script>\ |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 136 | <body style=\"font-family: sans-serif; font-size:25px; color:#807070\">\ |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 137 | <h1>PPP-Blinky WebSocket Test</h1>\ |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 138 | <div id=\"sts\">Idle</div>\ |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 139 | <button id=\"btn\" style=\"font-size: 100%; margin-top: 55px; margin-bottom: 55px;\">Connect</button>\ |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 140 | <h4><a href=\"/\">PPP-Blinky home</a></h4>\ |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 141 | </body>\ |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 142 | </html>"; // size = 916 bytes + 1 null byte = 917 bytes |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 143 | |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 144 | // The serial port on your mbed hardware. Your PC should be configured to view this port as a standard dial-up networking modem. |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 145 | // On Windows the model type of the modem should be selected as "Communications cable between two computers" |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 146 | // The modem baud rate should be set to 115200 baud |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 147 | // See instructions at the top. |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 148 | // On a typical mbed hardware platform this serial port is a USB virtual com port (VCP) and the USB serial driver is supplied by the board vendor. |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 149 | BufferedSerial pc(USBTX, USBRX, 100); // usb virtual com port for mbed hardware |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 150 | |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 151 | DigitalOut led1(LED1); // this led toggles when a packet is received |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 152 | |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 153 | // the standard hdlc frame start/end character. It's the tilde character "~" |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 154 | #define FRAME_7E (0x7e) |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 155 | |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 156 | /// a structure to keep all our ppp globals in |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 157 | struct pppType { |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 158 | int online; // we hunt for a PPP connection if this is zero |
| nixnax | 143:c5019f856a56 | 159 | int hostIP; // ip address of host |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 160 | int crc; // for calculating IP and TCP CRCs |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 161 | int ledState; // state of LED1 |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 162 | int httpPageCount; |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 163 | int firstFrame; // cleared after first frame |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 164 | struct { |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 165 | #define RXBUFLEN (1<<11) |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 166 | // the serial port receive buffer and packet buffer, size is RXBUFLEN (currently 2048 bytes) |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 167 | char buf[RXBUFLEN]; // RXBUFLEN MUST be a power of two because we use & operator for fast wrap-around in ring buffer |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 168 | int head; |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 169 | int tail; |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 170 | int rtail; |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 171 | int buflevel; |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 172 | } rx; // serial port objects |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 173 | struct { |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 174 | int len; // number of bytes in buffer |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 175 | int crc; // PPP CRC (frame check) |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 176 | #define PPP_max_size 2500 |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 177 | // we are assuming 1000 bytes more than MTU size of 1500 - due to the PPP encoding of special bytes |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 178 | char buf[PPP_max_size]; // send and receive buffer large enough for raw, encoded PPP/HDLC frames |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 179 | } pkt; // ppp buffer objects |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 180 | struct { |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 181 | int frameStartIndex; // frame start marker |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 182 | int frameEndIndex; // frame end marker |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 183 | } hdlc; // hdlc frame objects |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 184 | struct { |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 185 | unsigned int ident; // our IP ident value (outgoing frame count) |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 186 | } ip; // ip related object |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 187 | }; |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 188 | |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 189 | pppType ppp; // our global - definitely not thread safe |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 190 | |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 191 | /// Initialize the ppp structure and clear the receive buffer |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 192 | void pppInitStruct() |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 193 | { |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 194 | memset( ppp.rx.buf, 0, RXBUFLEN); |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 195 | ppp.online=0; |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 196 | ppp.rx.tail=0; |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 197 | ppp.rx.rtail=0; |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 198 | ppp.rx.head=0; |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 199 | ppp.rx.buflevel=0; |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 200 | ppp.pkt.len=0; |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 201 | ppp.ip.ident=10000; // easy to recognize in ip packet dumps |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 202 | ppp.ledState=0; |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 203 | ppp.hdlc.frameStartIndex=0; |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 204 | ppp.httpPageCount=0; |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 205 | ppp.firstFrame=1; |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 206 | } |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 207 | |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 208 | /// Toggle the LED on every second PPP packet received |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 209 | void led1Toggle() |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 210 | { |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 211 | led1 = (ppp.ledState >> 1) & 1; // use second bit, in other words toggle LED only every second packet |
| nixnax | 143:c5019f856a56 | 212 | ppp.ledState++; |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 213 | |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 214 | } |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 215 | |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 216 | /// returns 1 after a connect messasge, 0 at startup or after a disconnect message |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 217 | int connected() |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 218 | { |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 219 | return ppp.online; |
| nixnax | 143:c5019f856a56 | 220 | } |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 221 | |
| nixnax | 143:c5019f856a56 | 222 | /// Check for available characters from the PC and read them into our own circular serial receive buffer at ppp.rx.buf. |
| nixnax | 143:c5019f856a56 | 223 | /// Also, if we are offline and a 0x7e frame start character is seen, we go online immediately |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 224 | void checkPc() |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 225 | { |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 226 | char ch; |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 227 | if ( pc.readable() ) { |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 228 | int hd = (ppp.rx.head+1)&(RXBUFLEN-1); // increment/wrap head index |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 229 | if ( hd == ppp.rx.rtail ) { |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 230 | debugPrintf("\nReceive buffer full\n"); |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 231 | return; |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 232 | } |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 233 | ch = pc.getc(); // read new character |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 234 | ppp.rx.buf[ppp.rx.head] = ch; // insert in our receive buffer |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 235 | if ( ppp.online == 0 ) { |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 236 | if (ch == 0x7E) { |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 237 | ppp.online = 1; |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 238 | } |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 239 | } |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 240 | ppp.rx.head = hd; // update head pointer |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 241 | ppp.rx.buflevel++; |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 242 | } |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 243 | } |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 244 | |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 245 | /// print to debug port while checking for incoming characters |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 246 | void putcWhileCheckingInput( char outByte ) |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 247 | { |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 248 | #ifdef SERIAL_PORT_MONITOR_YES |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 249 | checkPc(); |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 250 | debugPutc( outByte ); |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 251 | checkPc(); |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 252 | #endif |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 253 | } |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 254 | |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 255 | /// puts to debug port while checking the PPP input stream |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 256 | void putsWhileCheckingInput( char * data ) |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 257 | { |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 258 | #ifdef SERIAL_PORT_MONITOR_YES |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 259 | char * nextChar = data; |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 260 | while( *nextChar != 0 ) { |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 261 | putcWhileCheckingInput( *nextChar ); // write one character to debug port while checking input |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 262 | nextChar++; |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 263 | } |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 264 | #endif |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 265 | } |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 266 | |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 267 | /// a sniffer tool to assist in figuring out where in the code we are having characters in the input buffer |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 268 | void qq() |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 269 | { |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 270 | if ( pc.readable() ) putsWhileCheckingInput( "Character available!\n" ); |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 271 | } |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 272 | |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 273 | /// Initialize the PPP CRC total |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 274 | void crcReset() |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 275 | { |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 276 | ppp.crc=0xffff; // crc restart |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 277 | } |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 278 | |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 279 | /// update the cumulative PPP CRC |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 280 | void crcDo(int x) |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 281 | { |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 282 | for (int i=0; i<8; i++) { |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 283 | ppp.crc=((ppp.crc&1)^(x&1))?(ppp.crc>>1)^0x8408:ppp.crc>>1; // crc calculator |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 284 | x>>=1; |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 285 | } |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 286 | checkPc(); // handle input |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 287 | } |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 288 | |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 289 | /// calculate the PPP CRC on an entire block of memory |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 290 | int crcBuf(char * buf, int size) // crc on an entire block of memory |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 291 | { |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 292 | crcReset(); |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 293 | for(int i=0; i<size; i++)crcDo(*buf++); |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 294 | return ppp.crc; |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 295 | } |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 296 | |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 297 | /// Get one character from our received PPP buffer |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 298 | int pc_getBuf() |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 299 | { |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 300 | int x = ppp.rx.buf[ ppp.rx.tail ]; |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 301 | ppp.rx.tail=(ppp.rx.tail+1)&(RXBUFLEN-1); |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 302 | ppp.rx.buflevel--; |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 303 | return x; |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 304 | } |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 305 | |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 306 | /// Dump a PPP frame to the debug serial port |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 307 | /// Note - the hex output of dumpPPPFrame() can be imported into WireShark |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 308 | /// Capture the frame's hex output in your terminal program and save as a text file |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 309 | /// In WireShark, use "Import Hex File". Options are: Offset=None, Protocol=PPP. |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 310 | void dumpPPPFrame() |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 311 | { |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 312 | char pbuf[30]; |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 313 | for(int i=0; i<ppp.pkt.len; i++) { |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 314 | checkPc(); |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 315 | sprintf(pbuf, "%02x ", ppp.pkt.buf[i]); |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 316 | checkPc(); |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 317 | putsWhileCheckingInput(pbuf); |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 318 | } |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 319 | checkPc(); |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 320 | sprintf(pbuf, " CRC=%04x Len=%d\n", ppp.pkt.crc, ppp.pkt.len); |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 321 | checkPc(); |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 322 | putsWhileCheckingInput(pbuf); |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 323 | } |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 324 | |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 325 | /// Process a received PPP frame |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 326 | void processPPPFrame(int start, int end) |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 327 | { |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 328 | led1Toggle(); // change led1 state on every frame we receive |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 329 | if(start==end) { |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 330 | return; // empty frame |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 331 | } |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 332 | crcReset(); |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 333 | char * dest = ppp.pkt.buf; |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 334 | ppp.pkt.len=0; |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 335 | int unstuff=0; |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 336 | int idx = start; |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 337 | while(1) { |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 338 | checkPc(); |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 339 | if (unstuff==0) { |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 340 | if (ppp.rx.buf[idx]==0x7d) unstuff=1; |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 341 | else { |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 342 | *dest = ppp.rx.buf[idx]; |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 343 | ppp.pkt.len++; |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 344 | dest++; |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 345 | crcDo(ppp.rx.buf[idx]); |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 346 | } |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 347 | } else { // unstuff characters prefixed with 0x7d |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 348 | *dest = ppp.rx.buf[idx]^0x20; |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 349 | ppp.pkt.len++; |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 350 | dest++; |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 351 | crcDo(ppp.rx.buf[idx]^0x20); |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 352 | unstuff=0; |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 353 | } |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 354 | idx = (idx+1) & (RXBUFLEN-1); |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 355 | if (idx == end) break; |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 356 | } |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 357 | ppp.pkt.crc = ppp.crc & 0xffff; |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 358 | if(0) dumpPPPFrame(); // set to 1 to dump ALL ppp frames |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 359 | if (ppp.pkt.crc == 0xf0b8) { // check for good CRC |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 360 | determinePacketType(); |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 361 | } else { |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 362 | #define REPORT_FCS_ERROR_YES |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 363 | #ifdef REPORT_FCS_ERROR_YES |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 364 | char pbuf[50]; // local print buffer |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 365 | checkPc(); |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 366 | sprintf(pbuf, "\nPPP FCS(crc) Error CRC=%x Length = %d\n",ppp.pkt.crc,ppp.pkt.len); // print a debug line |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 367 | checkPc(); |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 368 | putsWhileCheckingInput( pbuf ); |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 369 | if(0) dumpPPPFrame(); // set to 1 to dump frames with errors in them |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 370 | #endif |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 371 | } |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 372 | } |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 373 | |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 374 | /// output a character to the PPP port while checking for incoming characters |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 375 | void pcPutcWhileCheckingInput(int ch) |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 376 | { |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 377 | checkPc(); // check input |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 378 | pc.putc(ch); |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 379 | checkPc(); |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 380 | } |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 381 | |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 382 | /// do PPP HDLC-like handling of special (flag) characters |
| nixnax | 143:c5019f856a56 | 383 | void hdlcPut(int ch) |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 384 | { |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 385 | if ( (ch<0x20) || (ch==0x7d) || (ch==0x7e) ) { |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 386 | pcPutcWhileCheckingInput(0x7d); |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 387 | pcPutcWhileCheckingInput(ch^0x20); // these characters need special handling |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 388 | } else { |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 389 | pcPutcWhileCheckingInput(ch); |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 390 | } |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 391 | } |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 392 | |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 393 | /// send a PPP frame in HDLC format |
| nixnax | 143:c5019f856a56 | 394 | void send_pppFrame() |
| nixnax | 143:c5019f856a56 | 395 | { |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 396 | int crc = crcBuf(ppp.pkt.buf, ppp.pkt.len-2); // update crc |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 397 | ppp.pkt.buf[ ppp.pkt.len-2 ] = (~crc>>0); // fcs lo (crc) |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 398 | ppp.pkt.buf[ ppp.pkt.len-1 ] = (~crc>>8); // fcs hi (crc) |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 399 | pcPutcWhileCheckingInput(0x7e); // hdlc start-of-frame "flag" |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 400 | for(int i=0; i<ppp.pkt.len; i++) { |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 401 | wait_us(86); // wait one character time |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 402 | checkPc(); |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 403 | hdlcPut( ppp.pkt.buf[i] ); // send a character |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 404 | } |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 405 | pcPutcWhileCheckingInput(0x7e); // hdlc end-of-frame "flag" |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 406 | } |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 407 | |
| nixnax | 143:c5019f856a56 | 408 | /// convert a network ip address in the buffer to an integer (IP adresses are big-endian, i.e most significant byte first) |
| nixnax | 143:c5019f856a56 | 409 | int bufferToIP(char * buffer) |
| nixnax | 143:c5019f856a56 | 410 | { |
| nixnax | 143:c5019f856a56 | 411 | int result=0; |
| nixnax | 143:c5019f856a56 | 412 | for(int i=0; i<4; i++) result = (result<<8)|(*buffer++ & 0xff); |
| nixnax | 143:c5019f856a56 | 413 | return result; |
| nixnax | 143:c5019f856a56 | 414 | } |
| nixnax | 143:c5019f856a56 | 415 | |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 416 | /// handle IPCP configuration requests |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 417 | void ipcpConfigRequestHandler() |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 418 | { |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 419 | debugPrintf("Their IPCP Config Req, Our Ack\n"); |
| nixnax | 143:c5019f856a56 | 420 | if(ppp.pkt.buf[8]==3) { |
| nixnax | 143:c5019f856a56 | 421 | ppp.hostIP = bufferToIP(ppp.pkt.buf+10); |
| nixnax | 143:c5019f856a56 | 422 | debugPrintf("Host IP = %d.%d.%d.%d (%08x)\n", ppp.pkt.buf[10],ppp.pkt.buf[11],ppp.pkt.buf[12],ppp.pkt.buf[13],ppp.hostIP); |
| nixnax | 143:c5019f856a56 | 423 | } |
| nixnax | 143:c5019f856a56 | 424 | |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 425 | ppp.pkt.buf[4]=2; // change code to ack |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 426 | send_pppFrame(); // acknowledge everything they ask for - assume it's IP addresses |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 427 | |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 428 | debugPrintf("Our IPCP Ask (no options)\n"); |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 429 | ppp.pkt.buf[4]=1; // change code to request |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 430 | ppp.pkt.buf[7]=4; // no options in this request |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 431 | ppp.pkt.len=10; // no options in this request shortest ipcp packet possible (4 ppp + 4 ipcp + 2 crc) |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 432 | send_pppFrame(); // send our request |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 433 | } |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 434 | |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 435 | /// handle IPCP acknowledge (do nothing) |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 436 | void ipcpAckHandler() |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 437 | { |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 438 | debugPrintf("Their IPCP Grant\n"); |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 439 | } |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 440 | |
| nixnax | 143:c5019f856a56 | 441 | /// Handle IPCP NACK by sending our suggested IP address if there is an IP involved. |
| nixnax | 143:c5019f856a56 | 442 | /// This is how Linux responds to an IPCP request with no options - Windows assumes any IP address on the submnet is OK. |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 443 | void ipcpNackHandler() |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 444 | { |
| nixnax | 143:c5019f856a56 | 445 | debugPrintf("Their IPCP Nack"); |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 446 | if (ppp.pkt.buf[8]==3) { // check if the NACK contains an IP address parameter |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 447 | ppp.pkt.buf[4]=1; // assume the NACK contains our "suggested" IP address |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 448 | send_pppFrame(); // let's request this IP address as ours |
| nixnax | 143:c5019f856a56 | 449 | debugPrintf("Our IPCP ACK (received an IP)\n"); |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 450 | } // if it's not an IP nack we ignore it |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 451 | } |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 452 | |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 453 | /// handle all other IPCP requests (by ignoring them) |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 454 | void ipcpDefaultHandler() |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 455 | { |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 456 | debugPrintf("Their IPCP Other\n"); |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 457 | } |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 458 | |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 459 | /// process an incoming IPCP packet |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 460 | void IPCPframe() |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 461 | { |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 462 | int code = ppp.pkt.buf[4]; // packet type is here |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 463 | switch (code) { |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 464 | case 1: |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 465 | ipcpConfigRequestHandler(); |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 466 | break; |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 467 | case 2: |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 468 | ipcpAckHandler(); |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 469 | break; |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 470 | case 3: |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 471 | ipcpNackHandler(); |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 472 | break; |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 473 | default: |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 474 | ipcpDefaultHandler(); |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 475 | } |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 476 | } |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 477 | |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 478 | /// process an incoming UDP packet |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 479 | void UDPpacket() |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 480 | { |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 481 | char * udpPkt = ppp.pkt.buf+4; // udp packet start |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 482 | int headerSizeIP = (( udpPkt[0]&0xf)*4); |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 483 | char * udpBlock = udpPkt + headerSizeIP; // udp info start |
| nixnax | 143:c5019f856a56 | 484 | char * udpInf = udpBlock+8; // actual start of info |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 485 | #ifdef SERIAL_PORT_MONITOR_YES |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 486 | char * udpSrc = udpBlock; // source port |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 487 | char * udpDst = udpBlock+2; // destination port |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 488 | char * udpLen = udpBlock+4; // udp data length |
| nixnax | 143:c5019f856a56 | 489 | char * srcIP = udpPkt+12; // udp src addr |
| nixnax | 143:c5019f856a56 | 490 | char * dstIP = udpPkt+16; // udp dst addr |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 491 | int srcPort = (udpSrc[0]<<8) | udpSrc[1]; |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 492 | int dstPort = (udpDst[0]<<8) | udpDst[1]; |
| nixnax | 143:c5019f856a56 | 493 | int udpLength = ((udpLen[0]<<8) | udpLen[1]) - 8; // size of the actual udp data |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 494 | if(v0) debugPrintf("UDP %d.%d.%d.%d:%d ", srcIP[0],srcIP[1],srcIP[2],srcIP[3],srcPort); |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 495 | if(v0) debugPrintf("%d.%d.%d.%d:%d ", dstIP[0],dstIP[1],dstIP[2],dstIP[3],dstPort); |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 496 | if(v0) debugPrintf("Len %03d", udpLength); |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 497 | if (v1) { |
| nixnax | 143:c5019f856a56 | 498 | int printSize = udpLength; |
| nixnax | 143:c5019f856a56 | 499 | if (printSize > 20) printSize = 20; // print only first 20 characters |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 500 | for (int i=0; i<printSize; i++) { |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 501 | char ch = udpInf[i]; |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 502 | if (ch>31 && ch<127) { |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 503 | debugPrintf("%c", ch); |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 504 | } else { |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 505 | debugPrintf("_"); |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 506 | } |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 507 | } |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 508 | } |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 509 | if (v0) debugPrintf("\n"); |
| nixnax | 143:c5019f856a56 | 510 | #endif |
| nixnax | 143:c5019f856a56 | 511 | if (strncmp(udpInf,"echo ", 5) == 5) debugPrintf("echo found\n"); |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 512 | } |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 513 | |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 514 | /// perform a 16-bit checksum. if the byte count is odd, stuff in an extra zero byte. |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 515 | unsigned int dataCheckSum(unsigned char * ptr, int len) |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 516 | { |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 517 | unsigned int i,hi,lo,sum; |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 518 | unsigned char placeHolder; |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 519 | if (len&1) { |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 520 | placeHolder = ptr[len]; |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 521 | ptr[len]=0; // if the byte count is odd, insert one extra zero byte is after the last real byte because we sum byte PAIRS |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 522 | } |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 523 | sum=0; |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 524 | i=0; |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 525 | while ( i<len ) { |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 526 | checkPc(); |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 527 | hi = ptr[i++]; |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 528 | lo = ptr[i++]; |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 529 | sum = sum + ( (hi<<8) | lo ); |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 530 | } |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 531 | if (len&1) { |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 532 | ptr[len] = placeHolder; // restore the extra byte we made zero |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 533 | } |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 534 | sum = (sum & 0xffff) + (sum>>16); |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 535 | sum = (sum & 0xffff) + (sum>>16); // sum one more time to catch any carry from the carry |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 536 | return ~sum; |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 537 | } |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 538 | |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 539 | /// perform the checksum on an IP header |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 540 | void headerCheckSum() |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 541 | { |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 542 | int len =(ppp.pkt.buf[4]&0xf)*4; // length of header in bytes |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 543 | char * ptr = ppp.pkt.buf+4; // start of ip packet |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 544 | int sum=0; |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 545 | |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 546 | for (int i=0; i<len/2; i++) { |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 547 | int hi = *ptr; |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 548 | ptr++; |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 549 | int lo = *ptr; |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 550 | ptr++; |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 551 | int val = ( lo & 0xff ) | ( (hi<<8) & 0xff00 ); |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 552 | sum = sum + val; |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 553 | checkPc(); |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 554 | } |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 555 | sum = sum + (sum>>16); |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 556 | sum = ~sum; |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 557 | ppp.pkt.buf[14]= (sum>>8); |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 558 | ppp.pkt.buf[15]= (sum ); |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 559 | } |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 560 | |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 561 | /// handle a PING ICMP (internet control message protocol) packet |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 562 | void ICMPpacket() // internet control message protocol |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 563 | { |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 564 | char * ipPkt = ppp.pkt.buf+4; // ip packet start |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 565 | char * pktLen = ipPkt+2; |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 566 | int packetLength = (pktLen[0]<<8) | pktLen[1]; // icmp packet length |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 567 | int headerSizeIP = (( ipPkt[0]&0xf)*4); |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 568 | char * icmpType = ipPkt + headerSizeIP; // icmp data start |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 569 | char * icmpSum = icmpType+2; // icmp checksum |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 570 | #define ICMP_TYPE_PING_REQUEST 8 |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 571 | if ( icmpType[0] == ICMP_TYPE_PING_REQUEST ) { |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 572 | char * ipTTL = ipPkt+8; // time to live |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 573 | ipTTL[0]--; // decrement time to live |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 574 | char * srcAdr = ipPkt+12; |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 575 | char * dstAdr = ipPkt+16; |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 576 | #ifdef SERIAL_PORT_MONITOR_YES |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 577 | int icmpIdent = (icmpType[4]<<8)|icmpType[5]; |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 578 | int icmpSequence = (icmpType[6]<<8)|icmpType[7]; |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 579 | if(1) { |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 580 | char pbuf[50]; |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 581 | checkPc(); |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 582 | sprintf(pbuf, "ICMP PING %d.%d.%d.%d %d.%d.%d.%d ", srcAdr[0],srcAdr[1],srcAdr[2],srcAdr[3],dstAdr[0],dstAdr[1],dstAdr[2],dstAdr[3]); |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 583 | putsWhileCheckingInput( pbuf ); |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 584 | checkPc(); |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 585 | sprintf(pbuf, "Ident %04x Sequence %04d \n",icmpIdent,icmpSequence); |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 586 | checkPc(); |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 587 | putsWhileCheckingInput( pbuf ); |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 588 | } |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 589 | #endif |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 590 | char src[4]; |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 591 | char dst[4]; |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 592 | memcpy(src, srcAdr,4); |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 593 | memcpy(dst, dstAdr,4); |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 594 | memcpy(srcAdr, dst,4); |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 595 | memcpy(dstAdr, src,4); // swap src & dest ip |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 596 | char * chkSum = ipPkt+10; |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 597 | chkSum[0]=0; |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 598 | chkSum[1]=0; |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 599 | headerCheckSum(); // new ip header checksum |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 600 | #define ICMP_TYPE_ECHO_REPLY 0 |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 601 | icmpType[0]=ICMP_TYPE_ECHO_REPLY; // icmp echo reply |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 602 | icmpSum[0]=0; |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 603 | icmpSum[1]=0; // zero the checksum for recalculation |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 604 | int icmpLength = packetLength - headerSizeIP; // length of ICMP data portion |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 605 | unsigned int sum = dataCheckSum( (unsigned char *)icmpType, icmpLength); // this checksum on icmp data portion |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 606 | icmpSum[0]=(sum>>8)&0xff; |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 607 | icmpSum[1]=(sum )&0xff; // new checksum for ICMP data portion |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 608 | |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 609 | int printSize = icmpLength-8; // exclude size of icmp header |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 610 | char * icmpData = icmpType+8; // the actual payload data is after the header |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 611 | if (printSize > 10) printSize = 10; // print up to 20 characters |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 612 | if (0) { |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 613 | for (int i=0; i<printSize; i++) { |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 614 | char ch = icmpData[i]; |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 615 | if (ch>31 && ch<127) { |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 616 | putcWhileCheckingInput(ch); |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 617 | } else { |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 618 | putcWhileCheckingInput('_'); |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 619 | } |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 620 | } |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 621 | putcWhileCheckingInput('\n'); |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 622 | } |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 623 | send_pppFrame(); // reply to the ping |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 624 | } else { |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 625 | if (v0) { |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 626 | debugPrintf("ICMP type=%d \n", icmpType[0]); |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 627 | } |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 628 | } |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 629 | } |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 630 | |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 631 | /// handle an IGMP (internet group managment protocol) packet (by ignoring it) |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 632 | void IGMPpacket() |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 633 | { |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 634 | if (v0) debugPrintf("IGMP type=%d \n", ppp.pkt.buf[28]); |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 635 | } |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 636 | |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 637 | /// dump the header of an IP pakcet on the (optional) debug serial port |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 638 | void dumpHeaderIP (int outGoing) |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 639 | { |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 640 | #if defined(IP_HEADER_DUMP_YES) && defined(SERIAL_PORT_MONITOR_YES) |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 641 | checkPc(); // we are expecting the first character of the next packet |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 642 | char * ipPkt = ppp.pkt.buf+4; // ip packet start |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 643 | char * ident = ipPkt+4; // 2 bytes |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 644 | #ifdef UNUSED_IP_VARIABLES |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 645 | char * srcAdr = ipPkt+12; // 4 bytes |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 646 | char * dstAdr = ipPkt+16; // 4 bytes = total of 20 bytes |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 647 | char * version = ipPkt; // top 4 bits |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 648 | char * ihl = ipPkt; // bottom 4 bits |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 649 | char * dscp = ipPkt+1; // top 6 bits |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 650 | char * ecn = ipPkt+1; // lower 2 bits |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 651 | char * pktLen = ipPkt+2; // 2 bytes |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 652 | char * flags = ipPkt+6; // 2 bits |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 653 | char * ttl = ipPkt+8; // 1 byte |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 654 | char * protocol = ipPkt+9; // 1 byte |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 655 | char * headercheck= ipPkt+10; // 2 bytes |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 656 | int versionIP = (version[0]>>4)&0xf; |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 657 | int headerSizeIP = (ihl[0]&0xf)*4; |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 658 | int dscpIP = (dscp[0]>>2)&0x3f; |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 659 | int ecnIP = ecn[0]&3; |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 660 | int packetLength = (pktLen[0]<<8)|pktLen[1]; // ip total packet length |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 661 | int flagsIP = flags[0]>>14&3; |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 662 | int ttlIP = ttl[0]; |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 663 | int protocolIP = protocol[0]; |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 664 | unsigned int checksumIP = (headercheck[0]<<8)|headercheck[1]; |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 665 | #endif |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 666 | int IPv4Id = (ident[0]<<8)|ident[1]; |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 667 | char pbuf[50]; // local print buffer |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 668 | int n=0; |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 669 | n=n+sprintf(pbuf+n, outGoing ? "\x1b[34m" : "\x1b[30m" ); // VT100 color code, print black for incoming, blue for outgoing headers |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 670 | n=n+sprintf(pbuf+n, "%05d ",IPv4Id); // IPv4Id is a good way to correlate our dumps with net monitor or wireshark traces |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 671 | #define DUMP_FULL_IP_ADDRESS_YES |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 672 | #ifdef DUMP_FULL_IP_ADDRESS_YES |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 673 | char * srcAdr = ipPkt+12; // 4 bytes |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 674 | char * dstAdr = ipPkt+16; // 4 bytes = total of 20 bytes |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 675 | n=n+sprintf(pbuf+n, " %d.%d.%d.%d %d.%d.%d.%d ",srcAdr[0],srcAdr[1],srcAdr[2],srcAdr[3], dstAdr[0],dstAdr[1],dstAdr[2],dstAdr[3]); // full ip addresses |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 676 | #endif |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 677 | putsWhileCheckingInput( pbuf ); |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 678 | #ifndef TCP_HEADER_DUMP_YES |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 679 | putsWhileCheckingInput('\x1b[30m\n'); // there is no TCP header dump, so terminate the line with \n and VT100 code for black |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 680 | #endif |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 681 | #endif |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 682 | } |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 683 | |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 684 | /// dump a TCP header on the optional debug serial port |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 685 | void dumpHeaderTCP(int outGoing) |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 686 | { |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 687 | #if defined(TCP_HEADER_DUMP_YES) && defined(SERIAL_PORT_MONITOR_YES) |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 688 | int headerSizeIP = (ppp.pkt.buf[4]&0xf)*4; // header size of ip portion |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 689 | char * tcpStart = ppp.pkt.buf+4+headerSizeIP; // start of tcp packet |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 690 | char * seqtcp = tcpStart + 4; // 4 bytes |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 691 | char * acktcp = tcpStart + 8; // 4 bytes |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 692 | char * flagbitstcp = tcpStart + 12; // 9 bits |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 693 | unsigned int seq = (seqtcp[0]<<24)|(seqtcp[1]<<16)|(seqtcp[2]<<8)|(seqtcp[3]); |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 694 | unsigned int ack = (acktcp[0]<<24)|(acktcp[1]<<16)|(acktcp[2]<<8)|(acktcp[3]); |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 695 | if (seq && ack) {} // shut up the compiler about unused variables |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 696 | int flags = ((flagbitstcp[0]&1)<<8)|flagbitstcp[1]; |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 697 | char flagInfo[9]; // text string presenting the 8 most important TCP flags |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 698 | #define PRINT_ALL_TCP_FLAGS_YES |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 699 | #ifdef PRINT_ALL_TCP_FLAGS_YES |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 700 | memset(flagInfo,'.', 8); // fill string with "........" |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 701 | flagInfo[8]=0; // null terminate string |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 702 | if (flags & (1<<0)) flagInfo[7]='F'; |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 703 | if (flags & (1<<1)) flagInfo[6]='S'; |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 704 | if (flags & (1<<2)) flagInfo[5]='R'; |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 705 | if (flags & (1<<3)) flagInfo[4]='P'; |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 706 | if (flags & (1<<4)) flagInfo[3]='A'; |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 707 | if (flags & (1<<5)) flagInfo[2]='U'; |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 708 | if (flags & (1<<6)) flagInfo[1]='E'; |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 709 | if (flags & (1<<7)) flagInfo[0]='C'; |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 710 | #else |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 711 | if (flags & (1<<4)) flagInfo[0]='A'; // choose the most important flag to print |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 712 | if (flags & (1<<1)) flagInfo[0]='S'; |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 713 | if (flags & (1<<0)) flagInfo[0]='F'; |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 714 | if (flags & (1<<3)) flagInfo[0]='P'; |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 715 | if (flags & (1<<2)) flagInfo[0]='R'; |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 716 | flagInfo[1]=0; // ' ' |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 717 | flagInfo[2]=0; |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 718 | #endif |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 719 | putsWhileCheckingInput( flagInfo ); |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 720 | #define EVERY_PACKET_ON_A_NEW_LINE_YES |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 721 | #ifdef EVERY_PACKET_ON_A_NEW_LINE_YES |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 722 | putsWhileCheckingInput("\x1b[30m\n"); // write a black color and newline after every packet |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 723 | #endif |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 724 | if( outGoing && ( flags == 0x11 ) ) { // ACK/FIN - if this is an outgoing ACK/FIN its the end of a tcp conversation |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 725 | putcWhileCheckingInput('\n'); // insert an extra new line to mark the end of an HTTP the conversation |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 726 | } |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 727 | #endif |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 728 | } |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 729 | |
| nixnax | 143:c5019f856a56 | 730 | /// Encode a buffer in base-64 |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 731 | void enc64(char * in, char * out, int len) |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 732 | { |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 733 | const static char lut [] = "ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZabcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyz0123456789+/="; |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 734 | int i,j,a,b,c; |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 735 | i=0; |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 736 | j=0; |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 737 | while(1) { |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 738 | if (i<len) { |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 739 | a = in[i++]; |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 740 | out[j++] = lut[ ( (a >> 2) & 0x3f) ]; |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 741 | } else break; |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 742 | if (i<len) { |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 743 | b = in[i++]; |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 744 | out[j++] = lut[ ( (a << 4) & 0x30) | ( (b >> 4) & 0x0f) ]; |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 745 | out[j++] = lut[ ( (b << 2) & 0x3c) ]; |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 746 | } else out[j++] = '='; |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 747 | if (i<len) { |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 748 | c = in[i++]; |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 749 | j--; |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 750 | out[j++] = lut[ ( (b << 2) & 0x3c) | ( (c >> 6) & 0x03) ]; |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 751 | out[j++] = lut[ ( (c >> 0) & 0x3f) ]; |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 752 | } else out[j++] = '='; |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 753 | } |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 754 | out[j]=0; |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 755 | } |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 756 | |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 757 | /// handle a request for an http websocket |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 758 | /// we end up here if we enter the following javascript in a web browser console: x = new WebSocket("ws://172.10.10.2"); |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 759 | int webSocketHandler(char * dataStart) |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 760 | { |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 761 | int n=0; // byte counter |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 762 | char * key = strstr(dataStart, "Sec-WebSocket-Key: "); // search for the key in the payload |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 763 | if (key != NULL) { |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 764 | if (v0) putsWhileCheckingInput("WebSocket Request\n"); |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 765 | char challenge [70]; |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 766 | strncpy(challenge,key+19,70); // a local buffer |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 767 | *strchr(challenge,'\r')=0; // insert null so we can use sprintf |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 768 | strncat(challenge,"258EAFA5-E914-47DA-95CA-C5AB0DC85B11",70); // append websocket gui code |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 769 | char shaOutput [20]; // sha1 output |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 770 | sha1( shaOutput, challenge, strlen(challenge)); |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 771 | char encOut[50]; |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 772 | enc64( shaOutput, encOut, 20); |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 773 | char * versionstring = strstr(dataStart, "Sec-WebSocket-Version:"); |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 774 | char * version = challenge; |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 775 | strncpy(version, versionstring,70); // copy version string |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 776 | *strchr(version,'\r')=0; // null terminate so we can sprintf it |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 777 | memset(dataStart,0,500); // blank out old data befor send the websocket response header |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 778 | n=n+sprintf(dataStart+n, "HTTP/1.1 101 Switching Protocols\r\n"); |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 779 | n=n+sprintf(dataStart+n, "Upgrade: websocket\r\n"); |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 780 | n=n+sprintf(dataStart+n, "Connection: Upgrade\r\n"); |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 781 | n=n+sprintf(dataStart+n, "Sec-WebSocket-Accept: %s\r\n",encOut); |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 782 | n=n+sprintf(dataStart+n, "%s\r\n",version); |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 783 | n=n+sprintf(dataStart+n, "mbed-Code: PPP-Blinky\r\n"); |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 784 | n=n+sprintf(dataStart+n, "\r\n"); // websocket response header ending |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 785 | } |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 786 | return n; // this response should satisfy a web browser's websocket protocol request |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 787 | } |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 788 | |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 789 | #define TCP_FLAG_ACK (1<<4) |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 790 | #define TCP_FLAG_SYN (1<<1) |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 791 | #define TCP_FLAG_PSH (1<<3) |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 792 | #define TCP_FLAG_RST (1<<2) |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 793 | #define TCP_FLAG_FIN (1<<0) |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 794 | |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 795 | /// respond to an HTTP request |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 796 | int httpResponse(char * dataStart) |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 797 | { |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 798 | int n=0; // number of bytes we have printed so far |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 799 | n = webSocketHandler( dataStart ); // test for and handle WebSocket upgrade requests |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 800 | if (n>0) return n; // if it's a WebSocket we already have the response, so return |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 801 | |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 802 | int nHeader; // byte size of HTTP header |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 803 | int contentLengthStart; // index where HTML starts |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 804 | int httpGet5,httpGet6,httpGetx, httpGetRoot; // temporary storage of strncmp results |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 805 | |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 806 | ppp.httpPageCount++; // increment the number of frames we have made |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 807 | |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 808 | httpGetRoot = strncmp(dataStart, "GET / HTTP/1.", 13); // found a GET to the root directory |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 809 | httpGetx = strncmp(dataStart, "GET /x", 6); // found a GET to /x which we will treat special (anything starting with /x, e.g. /x, /xyz, /xABC?pqr=123 |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 810 | httpGet5 = dataStart[5]; // the first character in the path name, we use it for special functions later on |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 811 | httpGet6 = dataStart[6]; // the second character in the path name, we use it for special functions later on |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 812 | // for example, you could try this using netcat (nc): echo "GET /x" | nc 172.10.10.2 |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 813 | if( (httpGetRoot==0) || (httpGetx==0) ) { |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 814 | n=n+sprintf(n+dataStart,"HTTP/1.1 200 OK\r\nServer: mbed-PPP-Blinky-v1\r\n"); // 200 OK header |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 815 | } else { |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 816 | n=n+sprintf(n+dataStart,"HTTP/1.1 404 Not Found\r\nServer: mbed-PPP-Blinky\r\n"); // 404 header |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 817 | } |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 818 | n=n+sprintf(n+dataStart,"Content-Length: "); // http header |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 819 | contentLengthStart = n; // remember where Content-Length is in buffer |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 820 | n=n+sprintf(n+dataStart,"?????\r\n"); // leave five spaces for content length - will be updated later |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 821 | n=n+sprintf(n+dataStart,"Connection: close\r\n"); // close connection immediately |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 822 | n=n+sprintf(n+dataStart,"Content-Type: text/html; charset=us-ascii\r\n\r\n"); // http header must end with empty line (\r\n) |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 823 | nHeader=n; // size of HTTP header |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 824 | if( httpGetRoot == 0 ) { |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 825 | // this is where we insert our web page into the buffer |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 826 | memcpy(n+dataStart,rootWebPage,sizeof(rootWebPage)); |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 827 | n = n + sizeof(rootWebPage)-1; // one less than sizeof because we don't count the null byte at the end |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 828 | } else if ( (httpGet5 == 'w') && (httpGet6 == 's') ) { // "ws" is a special page for websocket demo |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 829 | memcpy(n+dataStart,webSocketPage,sizeof(webSocketPage)); |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 830 | n = n + sizeof(webSocketPage)-1; // one less than size |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 831 | } else { |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 832 | if (httpGetx == 0) { // the page request started with "GET /x" - here we treat anything starting with /x special: |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 833 | |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 834 | #define W3C_COMPLIANT_RESPONSE_NO |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 835 | // change the above to W3C_COMPLIANT_RESPONSE_YES if you want a W3C.org compliant HTTP response |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 836 | #ifdef W3C_COMPLIANT_RESPONSE_YES |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 837 | n=n+sprintf(n+dataStart,"<!DOCTYPE html><title>mbed PPP-Blinky</title>"); // html title (W3C.org required elements) |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 838 | n=n+sprintf(n+dataStart,"<body>%d</body>",ppp.httpPageCount); // body = the http frame count |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 839 | #else |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 840 | if( httpGet6 == 'b' ) { // if the fetched page is "xb" send a meta command to let the browser continuously reload |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 841 | n=n+sprintf(n+dataStart, "<meta http-equiv=\"refresh\" content=\"0\">"); // reload loop - handy for benchmarking |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 842 | } |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 843 | // /x is a very short page, in fact, it is only a decimal number showing the http Page count |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 844 | n=n+sprintf(n+dataStart,"%d ",ppp.httpPageCount); // not really valid html but most browsers and curl are ok with it |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 845 | #endif |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 846 | } else { |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 847 | // all other requests get 404 Not Found response with a http frame count - nice for debugging |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 848 | n=n+sprintf(n+dataStart,"<!DOCTYPE html><title>mbed PPP-Blinky</title>"); // html title (required element) |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 849 | n=n+sprintf(n+dataStart,"<body>Not Found</body>"); // not found message |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 850 | } |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 851 | } |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 852 | #define CONTENTLENGTHSIZE 5 |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 853 | char contentLengthString[CONTENTLENGTHSIZE+1]; |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 854 | snprintf(contentLengthString,CONTENTLENGTHSIZE+1,"%*d",CONTENTLENGTHSIZE,n-nHeader); // print Content-Length with leading spaces and fixed width equal to csize |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 855 | memcpy(dataStart+contentLengthStart, contentLengthString, CONTENTLENGTHSIZE); // copy Content-Length to it's place in the send buffer |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 856 | return n; // total byte size of our response |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 857 | } |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 858 | |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 859 | /// handle TCP data that is not an HTTP get |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 860 | /// this is the response if we have TCP data but it's not an HTTP GET |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 861 | /// this is handy when you for example want to use netcat (nc.exe) to talk to PPP-Blinky |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 862 | /// this could also be a websocket receive event - especially if the first byte is 0x81 (websocket data push) |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 863 | int tcpResponse(char * dataStart, int len, int * outFlags) |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 864 | { |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 865 | int n=0; // number of bytes we have printed so far |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 866 | if (dataStart[0] == 0x81) { // check if this is a websocket push message |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 867 | // this is most likely a websocket push message. you get this when you enter this in your browser console: x.send("my message"); |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 868 | if (0) putsWhileCheckingInput( "Got data from websocket send()\n" ); |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 869 | |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 870 | // for now we simply echo the websocket data back to the client - the client should therefore see an onmessage event |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 871 | // to display the echoed data in your browser, enter the following into the browser console: x.onmessage = function(msg){ console.log( msg.data ); } |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 872 | if (1) { |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 873 | char mask [4]; |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 874 | memcpy ( mask, dataStart+2, 4); // websocket messages are "masked", so first we obtain the 4-byte mask |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 875 | int websocketMessageSize = len - 6; // 1 byte prefix (0x81), 1 byte, 4 bytes mask = 6 bytes |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 876 | if((dataStart[1]&0x80)==0x80) // test if the mask bit is set, which means all data is xor'ed with the mask |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 877 | for (int i=0; i<websocketMessageSize; i++) dataStart[i+6]^= mask[i%4]; // unmask each byte with one of the mask bytes |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 878 | dataStart[1] = len-2; // add four extra bytes to the message length because we don't use mask bytes for the send |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 879 | memcpy(dataStart+2, "Got:",4); // insert our own text into the four mask bytes |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 880 | n = len; // our response size remains exactly the same length as what we received |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 881 | } |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 882 | } else if ( (dataStart[0]==0x88) && (dataStart[1]==0x80) && (len == 6) ) { // test for a websocket close request |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 883 | n=2; // our close command is only two bytes long because we don't use the four mask bytes |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 884 | dataStart[1]=0; // we don't have mask bytes on |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 885 | } else if (v1) putsWhileCheckingInput("TCP data received\n"); |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 886 | return n; // total byte size of our response |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 887 | } |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 888 | |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 889 | /// handle an incoming TCP packet |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 890 | /// use the first few bytes to figure out if it's a websocket, an http request or just pure incoming TCP data |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 891 | void tcpHandler() |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 892 | { |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 893 | // IP header |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 894 | char * ipPkt = ppp.pkt.buf+4; // ip packet start |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 895 | char * ihl = ipPkt; // bottom 4 bits |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 896 | char * pktLen = ipPkt+2; // 2 bytes |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 897 | char * ident = ipPkt+4; // 2 bytes |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 898 | char * protocol = ipPkt+9; // 1 byte |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 899 | char * headercheck= ipPkt+10; // 2 bytes |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 900 | char * srcAdr = ipPkt+12; // 4 bytes |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 901 | char * dstAdr = ipPkt+16; // 4 bytes = total of 20 bytes |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 902 | int headerSizeIP = (ihl[0]&0xf)*4; |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 903 | int packetLength = (pktLen[0]<<8)|pktLen[1]; // ip total packet length |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 904 | |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 905 | // TCP header |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 906 | char * tcp = ppp.pkt.buf+4+headerSizeIP; // start of tcp packet |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 907 | char * srctcp = tcp + 0; // 2 bytes |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 908 | char * dsttcp = tcp + 2; // 2 bytes |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 909 | char * seqtcp = tcp + 4; // 4 bytes |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 910 | char * acktcp = tcp + 8; // 4 bytes |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 911 | char * offset = tcp + 12; // 4 bits |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 912 | char * flagbitstcp = tcp + 12; // 9 bits |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 913 | char * windowsizetcp = tcp + 14; // 2 bytes |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 914 | char * checksumtcp = tcp + 16; // 2 bytes |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 915 | |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 916 | if(ident) {}; // shut up unused variable reference warning |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 917 | int tcpSize = packetLength - headerSizeIP; |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 918 | int headerSizeTCP = ((offset[0]>>4)&0x0f)*4; // size of tcp header only |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 919 | int protocolIP = protocol[0]; |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 920 | char * tcpDataIn = tcp + headerSizeTCP; // start of data block after TCP header |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 921 | int tcpDataSize = tcpSize - headerSizeTCP; // size of data block after TCP header |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 922 | char * tcpDataOut = tcp + 20; // start of outgoing data |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 923 | unsigned int seq_in = (seqtcp[0]<<24)|(seqtcp[1]<<16)|(seqtcp[2]<<8)|(seqtcp[3]); |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 924 | unsigned int ack_in = (acktcp[0]<<24)|(acktcp[1]<<16)|(acktcp[2]<<8)|(acktcp[3]); |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 925 | unsigned int ack_out = seq_in + tcpDataSize; |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 926 | unsigned int seq_out = ack_in; // use their version of our current sequence number |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 927 | |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 928 | // first we shorten the TCP response header to only 20 bytes. This means we ignore all TCP option requests |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 929 | tcpSize = 20; // shorten total TCP packet size to 20 bytes (no data) |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 930 | headerSizeTCP = 20; // shorten outgoing TCP header size 20 bytes |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 931 | offset[0] = (headerSizeTCP/4)<<4; // shorten tcp header size to 20 bytes |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 932 | packetLength = 40; // shorten total packet size to 40 bytes (20 ip + 20 tcp) |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 933 | pktLen[1] = 40; // set total packet size to 40 bytes (20 ip + 20 tcp) |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 934 | pktLen[0] = 0; // set total packet size to 40 bytes (20 ip + 20 tcp) |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 935 | |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 936 | int dataLen = 0; // most of our responses will have zero TCP data, only a header |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 937 | int flagsOut = TCP_FLAG_ACK; // the default case is an ACK packet |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 938 | int flagsTCP = ((flagbitstcp[0]&1)<<8)|flagbitstcp[1]; // the tcp flags we received |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 939 | windowsizetcp[0] = (700 >> 8 ); // tcp window size hi byte |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 940 | windowsizetcp[1] = (700 & 0xff); // tcp window size lo byte |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 941 | |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 942 | // A sparse TCP flag interpreter that implements stateless TCP connections |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 943 | |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 944 | switch ( flagsTCP ) { |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 945 | case TCP_FLAG_ACK: |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 946 | return; |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 947 | case TCP_FLAG_SYN: |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 948 | flagsOut = TCP_FLAG_SYN | TCP_FLAG_ACK; // something wants to connect - acknowledge it |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 949 | seq_out = seq_in+0x10000000U; // create a new sequence number using their sequence as a starting point, increase the highest digit |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 950 | ack_out++; // for SYN flag we have to increase the sequence by 1 |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 951 | break; |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 952 | case TCP_FLAG_ACK | TCP_FLAG_PSH: |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 953 | if ( (strncmp(tcpDataIn, "GET /", 5) == 0) ) { // check for an http GET command |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 954 | flagsOut = TCP_FLAG_ACK | TCP_FLAG_PSH; // set outgoing FIN flag to ask them to close from their side |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 955 | dataLen = httpResponse(tcpDataOut); // send an http response |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 956 | } else { |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 957 | dataLen = tcpResponse(tcpDataOut,tcpDataSize, &flagsOut); // not a web request, send a packet reporting number of received bytes |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 958 | } |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 959 | break; |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 960 | case TCP_FLAG_FIN: |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 961 | case TCP_FLAG_FIN | TCP_FLAG_ACK: |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 962 | case TCP_FLAG_FIN | TCP_FLAG_PSH | TCP_FLAG_ACK: |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 963 | flagsOut = TCP_FLAG_ACK | TCP_FLAG_FIN; // set outgoing FIN flag to ask them to close from their side |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 964 | ack_out++; // for FIN flag we have to increase the sequence by 1 |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 965 | break; |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 966 | default: |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 967 | return; // ignore remaining packets |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 968 | } // switch |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 969 | |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 970 | // The TCP flag handling is now done |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 971 | // first we swap source and destination TCP addresses and insert the new ack and seq numbers |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 972 | char tempHold[12]; // it's 12 long because we later reuse it when building the TCP pseudo-header |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 973 | memcpy(tempHold, srcAdr,4); |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 974 | memcpy(srcAdr, dstAdr,4); |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 975 | memcpy(dstAdr, tempHold,4); // swap ip address source/dest |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 976 | memcpy(tempHold, srctcp,2); |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 977 | memcpy(srctcp, dsttcp,2); |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 978 | memcpy(dsttcp, tempHold,2); // swap ip port source/dest |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 979 | |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 980 | acktcp[0]=ack_out>>24; |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 981 | acktcp[1]=ack_out>>16; |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 982 | acktcp[2]=ack_out>>8; |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 983 | acktcp[3]=ack_out>>0; // save ack 32-bit integer |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 984 | seqtcp[0]=seq_out>>24; |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 985 | seqtcp[1]=seq_out>>16; |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 986 | seqtcp[2]=seq_out>>8; |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 987 | seqtcp[3]=seq_out>>0; // save seq 32-bit integer |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 988 | |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 989 | flagbitstcp[1] = flagsOut; // update the TCP flags |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 990 | |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 991 | // increment our outgoing ip packet counter |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 992 | ppp.ip.ident++; // get next ident number for our packet |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 993 | |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 994 | // Now we recalculate all the header sizes |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 995 | tcpSize = headerSizeTCP + dataLen; // tcp packet size |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 996 | int newPacketSize = headerSizeIP + tcpSize; // calculate size of the outgoing packet |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 997 | pktLen[0] = (newPacketSize>>8); |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 998 | pktLen[1]=newPacketSize; // ip total packet size |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 999 | ppp.pkt.len = newPacketSize+4+2; // ip packet length + 4-byte ppp prefix (ff 03 00 21) + 2 fcs (crc) bytes bytes at the end of the packet |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 1000 | |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 1001 | // the header is all set up, now do the IP and TCP checksums |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 1002 | headercheck[0]=0; // IP header checksum |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 1003 | headercheck[1]=0; // IP header checksum |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 1004 | headerCheckSum(); // calculate the IP header checksum |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 1005 | |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 1006 | // now we have to build the so-called 12-byte TCP "pseudo-header" in front of the TCP header (containing some IP header values) in order to correctly calculate the TCP checksum |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 1007 | // this header contains the most important parts of the IP header, i.e. source and destination address, protocol number and data length. |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 1008 | char * pseudoHeader = tcp-12; // mark the start of the TCP pseudo-header |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 1009 | memcpy(tempHold, pseudoHeader, 12); // preserve the 12 bytes of the IP header where the TCP pseudo-Header will be built |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 1010 | memcpy( pseudoHeader+0, srcAdr, 8); // IP source and destination addresses from IP header |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 1011 | memset( pseudoHeader+8, 0, 1); // reserved, set to zero |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 1012 | memset( pseudoHeader+9, protocolIP, 1); // protocol from IP header |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 1013 | memset( pseudoHeader+10, tcpSize>>8, 1); // size of IP data (TCP packet size) |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 1014 | memset( pseudoHeader+11, tcpSize, 1); // size of IP data (TCP packet size) |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 1015 | |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 1016 | // pseudo-header built, now we can calculate TCP checksum |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 1017 | checksumtcp[0]=0; |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 1018 | checksumtcp[1]=0; |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 1019 | unsigned int pseudoHeaderSum=dataCheckSum((unsigned char *)pseudoHeader,tcpSize+12); // calculate the TCP checksum starting at the pseudo-header |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 1020 | checksumtcp[0]=pseudoHeaderSum>>8; |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 1021 | checksumtcp[1]=pseudoHeaderSum; |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 1022 | memcpy( tcp-12, tempHold, 12); // restore the 12 bytes that the pseudo-header overwrote |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 1023 | dumpHeaderIP(1); // dump outgoing IP header |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 1024 | dumpHeaderTCP(1); // dump outgoing TCP header |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 1025 | for (int i=0; i<45*1000/10; i++) { // 45 ms delay before sending frame - a typical internet delay time |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 1026 | checkPc(); // catch any incoming characters |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 1027 | wait_us(10); // wait less than 1 character duration at 115200 |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 1028 | } |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 1029 | send_pppFrame(); // All preparation complete - send the TCP response |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 1030 | if(0) dumpPPPFrame(); // set to 1 to dump transmitted ppp frame |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 1031 | memset(ppp.pkt.buf+44,0,500); // flush out traces of previous data that we may scan for |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 1032 | } |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 1033 | |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 1034 | |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 1035 | /// dump the TCP data to the debug serial port |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 1036 | void dumpDataTCP() |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 1037 | { |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 1038 | int ipPktLen = (ppp.pkt.buf[6]<<8)|ppp.pkt.buf[7]; // overall length of ip packet |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 1039 | int ipHeaderLen = (ppp.pkt.buf[4]&0xf)*4; // length of ip header |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 1040 | int headerSizeTCP = ((ppp.pkt.buf[4+ipHeaderLen+12]>>4)&0xf)*4;; // length of tcp header |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 1041 | int dataLen = ipPktLen - ipHeaderLen - headerSizeTCP; // data is what's left after the two headers |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 1042 | if (v1) { |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 1043 | char pbuf[50]; // local print buffer |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 1044 | checkPc(); |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 1045 | sprintf(pbuf, "TCP %d ipHeader %d tcpHeader %d Data %d\n", ipPktLen, ipHeaderLen, headerSizeTCP, dataLen); // 1 for more verbose |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 1046 | checkPc(); |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 1047 | putsWhileCheckingInput( pbuf ); |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 1048 | } |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 1049 | if (dataLen > 0) { |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 1050 | ppp.pkt.buf[4+ipHeaderLen+headerSizeTCP+dataLen]=0; // insert a null after the data so debug printf stops printing after the data |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 1051 | putsWhileCheckingInput( ppp.pkt.buf+4+ipHeaderLen+headerSizeTCP ); // print the tcp payload data |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 1052 | putsWhileCheckingInput("\n"); |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 1053 | } |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 1054 | } |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 1055 | |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 1056 | /// handle an incoming TCP packet |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 1057 | void TCPpacket() |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 1058 | { |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 1059 | dumpHeaderIP(0); // dump incoming packet header |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 1060 | dumpHeaderTCP(0); // dump incoming packet header |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 1061 | if (v2) dumpDataTCP(); |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 1062 | tcpHandler(); |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 1063 | } |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 1064 | |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 1065 | /// handle the remaining IP protocols by ignoring them |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 1066 | void otherProtocol() |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 1067 | { |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 1068 | debugPrintf("Other IP protocol"); |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 1069 | } |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 1070 | |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 1071 | /// process an incoming IP packet |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 1072 | void IPframe() |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 1073 | { |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 1074 | int protocol = ppp.pkt.buf[13]; |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 1075 | switch (protocol) { |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 1076 | case 1: |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 1077 | ICMPpacket(); |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 1078 | break; |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 1079 | case 2: |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 1080 | IGMPpacket(); |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 1081 | break; |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 1082 | case 17: |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 1083 | UDPpacket(); |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 1084 | break; |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 1085 | case 6: |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 1086 | TCPpacket(); |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 1087 | break; |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 1088 | default: |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 1089 | otherProtocol(); |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 1090 | } |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 1091 | } |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 1092 | |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 1093 | /// respond to LCP (line configuration protocol) configuration request) by allowing no options |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 1094 | void LCPconfReq() |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 1095 | { |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 1096 | debugPrintf("LCP Config "); |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 1097 | if (ppp.pkt.buf[7] != 4) { |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 1098 | ppp.pkt.buf[4]=4; // allow only "no options" which means Maximum Receive Unit (MRU) is default 1500 bytes |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 1099 | debugPrintf("Reject\n"); |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 1100 | send_pppFrame(); |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 1101 | } else { |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 1102 | ppp.pkt.buf[4]=2; // ack zero conf |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 1103 | debugPrintf("Ack\n"); |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 1104 | send_pppFrame(); |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 1105 | debugPrintf("LCP Ask\n"); |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 1106 | ppp.pkt.buf[4]=1; // request no options |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 1107 | send_pppFrame(); |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 1108 | } |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 1109 | } |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 1110 | |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 1111 | /// handle LCP acknowledge packets by ignoring them |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 1112 | void LCPconfAck() |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 1113 | { |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 1114 | debugPrintf("LCP Ack\n"); |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 1115 | } |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 1116 | |
| nixnax | 143:c5019f856a56 | 1117 | /// handle LCP end (disconnect) packets by acknowledging them and by setting ppp.online to false |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 1118 | void LCPend() |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 1119 | { |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 1120 | ppp.pkt.buf[4]=6; |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 1121 | send_pppFrame(); // acknowledge |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 1122 | ppp.online=0; // start hunting for connect string again |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 1123 | pppInitStruct(); // flush the receive buffer |
| nixnax | 143:c5019f856a56 | 1124 | debugPrintf("LCP End (Disconnect from host)\n"); |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 1125 | } |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 1126 | |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 1127 | /// respond to other LCP requests by ignoring them |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 1128 | void LCPother() |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 1129 | { |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 1130 | debugPrintf("LCP Other\n"); |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 1131 | dumpPPPFrame(); |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 1132 | } |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 1133 | |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 1134 | /// process incoming LCP packets |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 1135 | void LCPframe() |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 1136 | { |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 1137 | int code = ppp.pkt.buf[4]; |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 1138 | switch (code) { |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 1139 | case 1: |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 1140 | LCPconfReq(); |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 1141 | break; // config request |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 1142 | case 2: |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 1143 | LCPconfAck(); |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 1144 | break; // config ack |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 1145 | case 5: |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 1146 | LCPend(); |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 1147 | break; // end connection |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 1148 | default: |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 1149 | LCPother(); |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 1150 | } |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 1151 | } |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 1152 | |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 1153 | /// discard packets that are not IP, IPCP, or LCP |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 1154 | void discardedFrame() |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 1155 | { |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 1156 | if (v0) debugPrintf("Frame is not IP, IPCP or LCP: %02x %02x %02x %02x\n", ppp.pkt.buf[0],ppp.pkt.buf[1],ppp.pkt.buf[2],ppp.pkt.buf[3]); |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 1157 | } |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 1158 | |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 1159 | /// determine the packet type (IP, IPCP or LCP) of incoming packets |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 1160 | void determinePacketType() |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 1161 | { |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 1162 | if ( ppp.pkt.buf[0] != 0xff ) { |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 1163 | debugPrintf("byte0 != ff\n"); |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 1164 | return; |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 1165 | } |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 1166 | if ( ppp.pkt.buf[1] != 3 ) { |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 1167 | debugPrintf("byte1 != 3\n"); |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 1168 | return; |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 1169 | } |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 1170 | if ( ppp.pkt.buf[3] != 0x21 ) { |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 1171 | debugPrintf("byte2 != 21\n"); |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 1172 | return; |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 1173 | } |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 1174 | int packetType = ppp.pkt.buf[2]; |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 1175 | switch (packetType) { |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 1176 | case 0xc0: |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 1177 | LCPframe(); |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 1178 | break; // link control |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 1179 | case 0x80: |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 1180 | IPCPframe(); |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 1181 | break; // IP control |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 1182 | case 0x00: |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 1183 | IPframe(); |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 1184 | break; // IP itself |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 1185 | default: |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 1186 | discardedFrame(); |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 1187 | } |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 1188 | } |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 1189 | |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 1190 | /// scan the PPP serial input stream for frame start markers |
| nixnax | 143:c5019f856a56 | 1191 | void waitForPppFrame() |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 1192 | { |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 1193 | while(1) { |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 1194 | checkPc(); // handle received characters |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 1195 | if ( ppp.rx.head != ppp.rx.tail ) { |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 1196 | int oldTail = ppp.rx.tail; // remember where the character is located in the buffer |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 1197 | int rx = pc_getBuf(); // get the character |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 1198 | if (rx==FRAME_7E) { |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 1199 | if (ppp.firstFrame) { // is this the start of the first frame start |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 1200 | ppp.firstFrame=0; |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 1201 | ppp.rx.rtail = ppp.rx.tail; // update real-time tail with the virtual tail |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 1202 | ppp.hdlc.frameStartIndex = ppp.rx.tail; // remember where first frame started |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 1203 | } else { |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 1204 | ppp.hdlc.frameEndIndex=oldTail; // mark the frame end character |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 1205 | processPPPFrame(ppp.hdlc.frameStartIndex, ppp.hdlc.frameEndIndex); // process the frame |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 1206 | ppp.rx.rtail = ppp.rx.tail; // update real-time tail with the virtual tail |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 1207 | ppp.hdlc.frameStartIndex = ppp.rx.tail; // remember where next frame started |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 1208 | break; |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 1209 | } |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 1210 | } |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 1211 | } |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 1212 | } |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 1213 | } |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 1214 | |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 1215 | /// scan for a connect string ("CLIENT") from the host PC, if found, we set ppp.oline to true, which will the IP packet scanner |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 1216 | void scanForConnectString() |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 1217 | { |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 1218 | while(ppp.online == 0) { |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 1219 | checkPc(); // gather received characters |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 1220 | // search for Windows Dialup Networking "Direct Connection Between Two Computers" expected connect string |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 1221 | char * found1 = strstr( (char *)ppp.rx.buf, "CLIENT" ); |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 1222 | if (found1 != NULL) { |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 1223 | // respond with Windows Dialup networking expected "Direct Connection Between Two Computers" response string |
| nixnax | 143:c5019f856a56 | 1224 | if (v0) debugPrintf("Connected: Found connect string \"CLIENT\", sent \"CLIENTSERVER\"\n"); |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 1225 | pc.puts("CLIENTSERVER"); |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 1226 | ppp.online=1; // we are connected - set flag so we stop looking for the connect string |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 1227 | checkPc(); |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 1228 | } |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 1229 | } |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 1230 | } |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 1231 | |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 1232 | /// set the PPP and debug baud rates and initialize data structures |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 1233 | void initialize() |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 1234 | { |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 1235 | pc.baud(115200); // USB serial port to pc |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 1236 | debugBaudRate(115200); // baud rate for our (optional) debug port |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 1237 | debugPrintf("\x1b[2J\x1b[H\x1b[30mmbed PPP-Blinky HTTP & WebSocket server ready :)\n"); // VT100 codes for clear_screen, home, black_text - Tera Term is a handy VT100 terminal |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 1238 | pppInitStruct(); // initialize all the PPP properties |
| nixnax | 143:c5019f856a56 | 1239 | } |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 1240 | |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 1241 | /* |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 1242 | /// initialize, wait for the connect message, then start processing PPP frames |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 1243 | int main() |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 1244 | { |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 1245 | initialize(); |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 1246 | while(1) { |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 1247 | scanForConnectString(); // wait for connect from PC dial-up networking |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 1248 | while(ppp.online) { |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 1249 | waitForPppFrame(); // wait for a PPP frame |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 1250 | } |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 1251 | } |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 1252 | } |
| nixnax | 142:54d1543e23e5 | 1253 | */ |
 Nicolas Nackel
Nicolas Nackel