Accelerometer Controlled Motors via Wifly
Lab 4 ECE 4180 GaTech
By Lindsay Herron and Javier Ceballos-Leon
This demo requires the use of
- Two mbeds (one for client and one for server)
- Two WiFly RN-XV modules (one for client and one for server)
- LSM9DS1 Breakout for IMU Accelerometer data
- uLCD-144-G2
- Speaker
- H-Bridge
- Two DC Motors
- Robot Shell
- Power Supply
Server Setup
Requirements
- An mbed
- A WiFly RN-XV module
- LSM9DS1 Breakout for IMU Accelerometer data
- uLCD-144-G2
- Speaker
The below image shows the overall layout of the server.
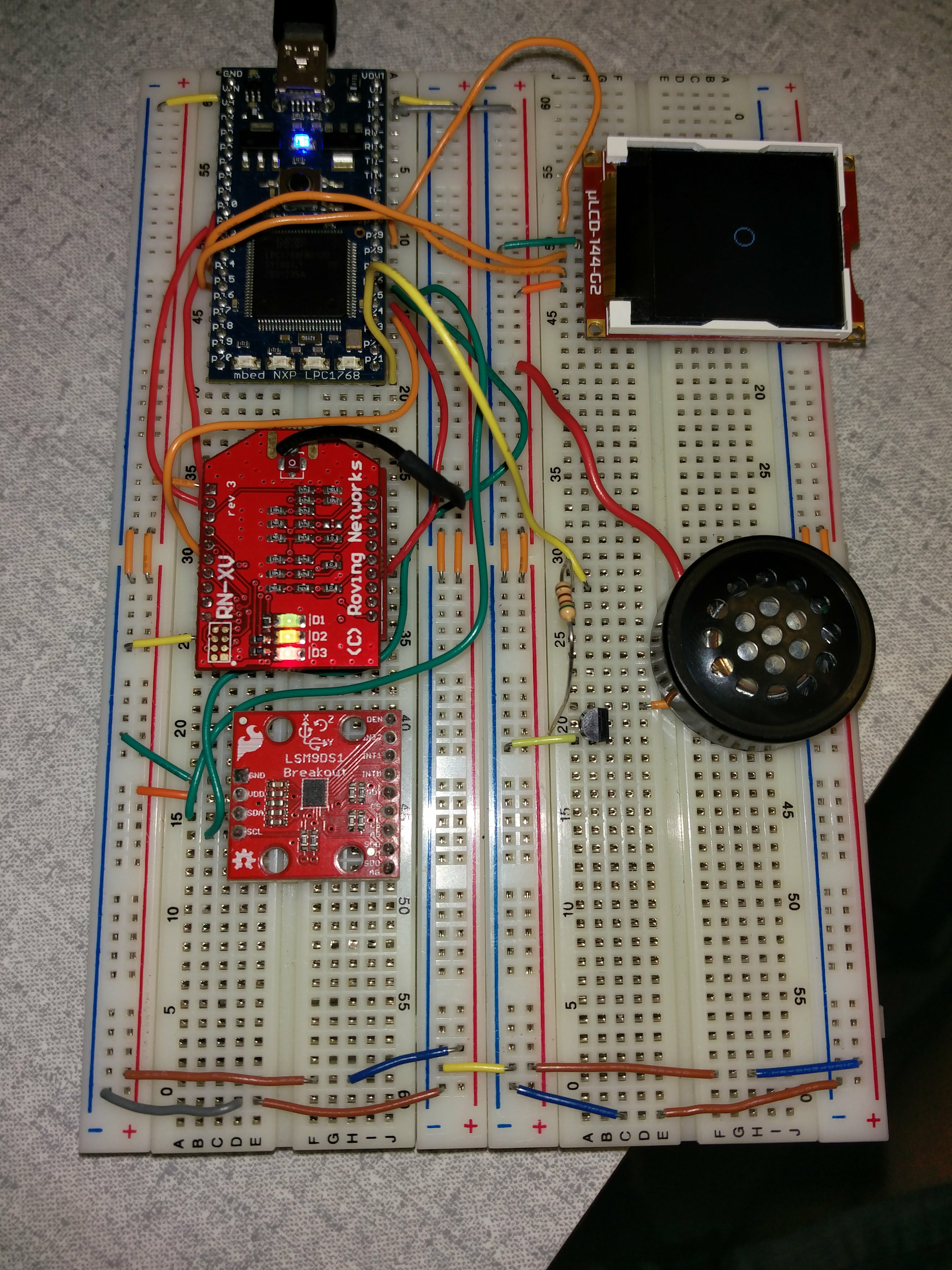
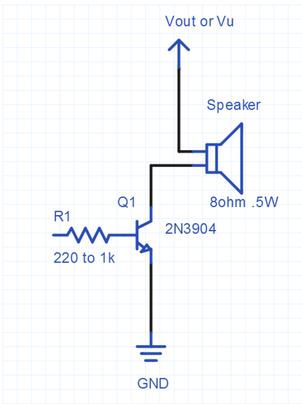
To connect the speaker, the below information is required to connect the driver circuit. Mbed pin 21 will be connected to the resistor below.
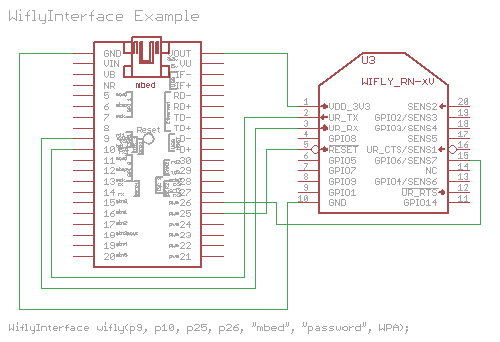
The wifly interface is shown below for wifly pin out, but the table will show what pin out was used from our side of the mbed.
The pin out of the server is shown below:
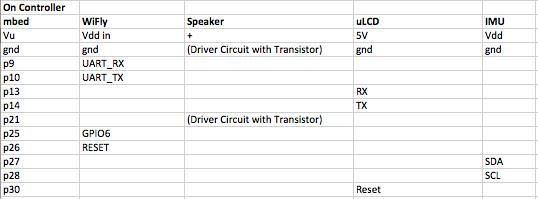
Client Setup
Requirements:
- An mbed
- A WiFly RN-XV module
- H-Bridge
- Two DC Motors
- Robot Shell
- Power Supply
The below image shows the overall client setup.
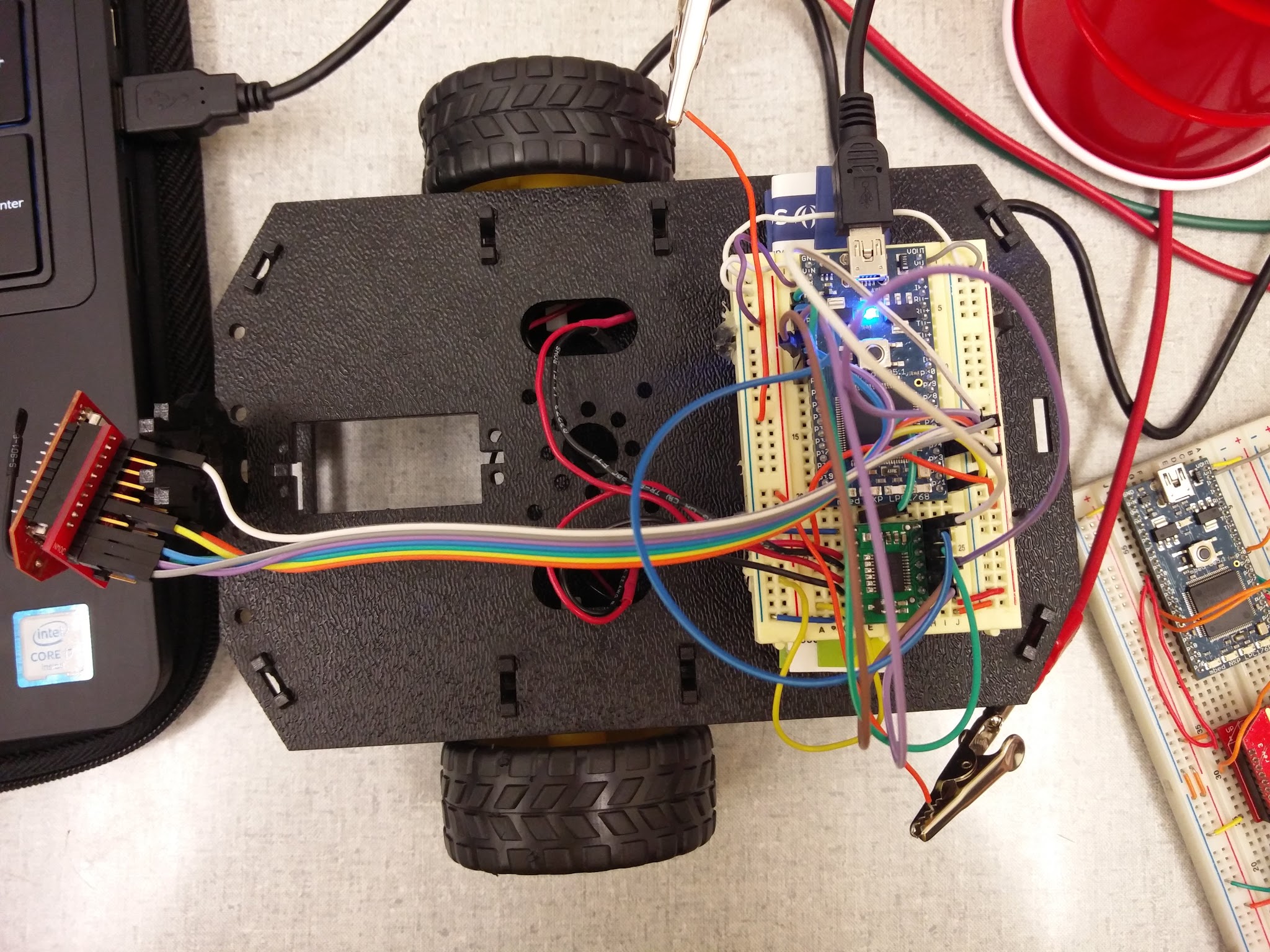
The wifly interface is shown below for wifly pin out, but the table will show what pin out was used from our side of the bed.

A power supply capable of 5V and 2A should work with this set-up, where + goes to the 5V rail and - goings to GND.
The pin out of the client is shown below:
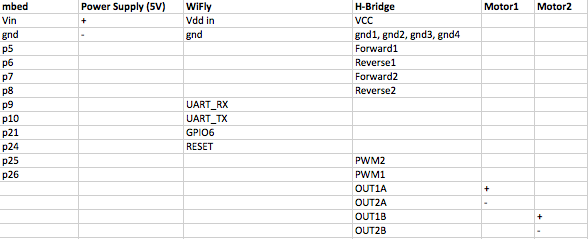
Below is the code to take the accelerometer and send the data to the client.
TCP Echo Server Using Wifly Sending IMU Accelerometer Data
#include "mbed.h"
#include "WiflyInterface.h"
#include "LSM9DS1.h"
#include "uLCD_4DGL.h"
#define ECHO_SERVER_PORT 7
#define PI 3.14159
#define DECLINATION -4.94
/* wifly object where:
* - p9 and p10 are for the serial communication
* - p25 is for the reset pin
* - p26 is for the connection status
* - "mbed" is the ssid of the network
* - "password" is the password
* - WPA is the security
*/
class Speaker
{
public:
Speaker(PinName pin) : _pin(pin) {
// _pin(pin) means pass pin to the Speaker Constructor
}
// class method to play a note based on PwmOut class
void PlayNote(float frequency, float duration, float volume) {
_pin.period(1.0/frequency);
_pin = volume/2.0;
wait(duration);
_pin = 0.0;
}
private:
// sets up specified pin for PWM using PwmOut class
PwmOut _pin;
};
Serial pc(USBTX, USBRX);
WiflyInterface wifly(p9, p10, p25, p26, "OnePlus2","password",WPA);//"ZETA", "vRinD87d", WPA);
uLCD_4DGL uLCD(p13, p14,p30);
float x = 64;
float y = 64;
float magX;
float magY;
float noteVal;
char buf[128];
int main (void)
{
Speaker mySpeaker(p21);
// loops forever playing two notes on speaker
uLCD.baudrate(3000000);
pc.printf("Party Started!!!");
wifly.init("192.168.43.140","255.255.255.0","192.168.43.1"); // do not use DHCP
while (!wifly.connect()); // join the network
pc.printf("IP Address is %s\n\r", wifly.getIPAddress());
TCPSocketServer server;
server.bind(ECHO_SERVER_PORT);
server.listen();
pc.printf("\nWait for new connection...\n");
TCPSocketConnection client;
server.accept(client);
/// init IMU
LSM9DS1 IMU(p28, p27, 0xD6, 0x3C);
IMU.begin();
if (!IMU.begin()) {
//pc.printf("Failed to communicate with LSM9DS1.\n");
}
IMU.calibrate();
while(1) {
while(!IMU.accelAvailable()){pc.printf("Failed Acc\n\r");};
IMU.readAccel();
x = IMU.ax;
y = IMU.ay;
//Level
uLCD.circle(64, 64, 7, WHITE);
uLCD.filled_circle(x/240+64, y/240+64, 5, WHITE);
wait(.075);
uLCD.filled_circle(x/240+64, y/240+64, 5, BLACK);
sprintf(buf,"%f/%f\n\r",x,y);
client.send_all(buf, 128);
//pc.printf("%s",buf);
noteVal =((fabsf(x)+fabsf(y))/18.285714286)+250;
//pc.printf("%f",noteVal);
mySpeaker.PlayNote(noteVal, 0.1, 0.1);
}
}
Below is the code that was used to control the motor.
TCP Echo Client Using Wifly Receiving Server Data and Controlling DC Motors via H-bridge
#include "WiflyInterface.h"
#include "mbed.h"
#include "string.h"
#include "stdio.h"
#include "ultrasonic.h"
DigitalOut rright(p6);
DigitalOut fright(p5);
DigitalOut rleft(p7);
DigitalOut fleft(p8);
DigitalOut LED(LED1);
PwmOut a(p26);
PwmOut b(p25);
Serial pc(USBTX, USBRX);
//Motion Control Functions
void forward(float a);
void reverse(float a);
void rotLeft(float a);
void rotRight(float a);
//Wifly
const char* ECHO_SERVER_ADDRESS = "192.168.43.140";
const int ECHO_SERVER_PORT = 7;
WiflyInterface wifly(p9, p10, p21, p24, "OnePlus2", "password", WPA);
//vars
float x=0;
float y=0;
int main()
{
char *p;//To split in_buffer
char *p1;
pc.printf("Party started");
wifly.init(); // use DHCP
while (!wifly.connect()); // join the network
pc.printf("IP Address is %s\n\r", wifly.getIPAddress());
TCPSocketConnection socket;
while (socket.connect(ECHO_SERVER_ADDRESS, ECHO_SERVER_PORT) < 0) {
pc.printf("Unable to connect to (%s) on port (%d)\r\n", ECHO_SERVER_ADDRESS, ECHO_SERVER_PORT);
wait(1);
}
socket.set_blocking(false, 1500);
char in_buffer[128];
while (1) {
int n = socket.receive(in_buffer, 128);
//pc.printf("%s\n\r", in_buffer);
p = strtok(in_buffer, "/");
p1 = strtok(NULL, "/");
x = (float) atof(p);
y = (float) atof(p1);
x = x/10000;//normalize
y = y/10000;//normalize
wait(0.1);
//pc.printf("x is %f y is %f\n\r", x, y);
//***************FORWARD**************
//RIGHT
if(x<0&&y<0) {
if(fabsf(x)>fabsf(y)) {
a= fabsf(y);
b= fabsf(x);
fright = 1;
fleft = 1;
rleft=0;
rright=0;
} else {
a= fabsf(y)-fabsf(x);
b= fabsf(y);
fright = 1;
fleft = 1;
rleft=0;
rright=0;
}
}
//LEFT
else if(x>0&&y<0) {
if(fabsf(x)>fabsf(y)) {
a=fabsf(x);
b=fabs(y);
fright = 1;
fleft = 1;
rleft=0;
rright=0;
} else {
a= fabsf(y);
b= fabsf(y)-fabsf(x);
fright = 1;
fleft = 1;
rleft=0;
rright=0;
}
}
//**************REVERSE*****************
//RIGHT
else if(x<0&&y>0) {
if(fabsf(x)>fabsf(y)) {
a= fabsf(y);
b = fabsf(x);
rright = 1;
rleft = 1;
fleft=0;
fright=0;
} else {
a = fabsf(y)- fabsf(x);
b = fabsf(y);
rright = 1;
rleft = 1;
fleft=0;
fright=0;
}
}
//LEFT
else if(x>0&&y>0) {
if(fabsf(x)>fabsf(y)) {
a= fabsf(x);
b= fabsf(y);
rright = 1;
rleft = 0;
fleft=0;
fright=0;
} else {
a = fabsf(y);
b = fabsf(y)- fabsf(x);
rright = 1;
rleft = 1;
fleft=0;
fright=0;
}
}
}
}
The below video shows a demo of this project.
Please log in to post comments.
