The official mbed C/C SDK provides the software platform and libraries to build your applications.
Fork of mbed by
(01.May.2014) started sales! http://www.switch-science.com/catalog/1717/
(13.March.2014) updated to 0.5.0
This is a pin conversion PCB from mbed 1768/11U24 to arduino UNO.
- So if you have both mbed and arduino shields, I guess you would be happy with such a conversion board :)
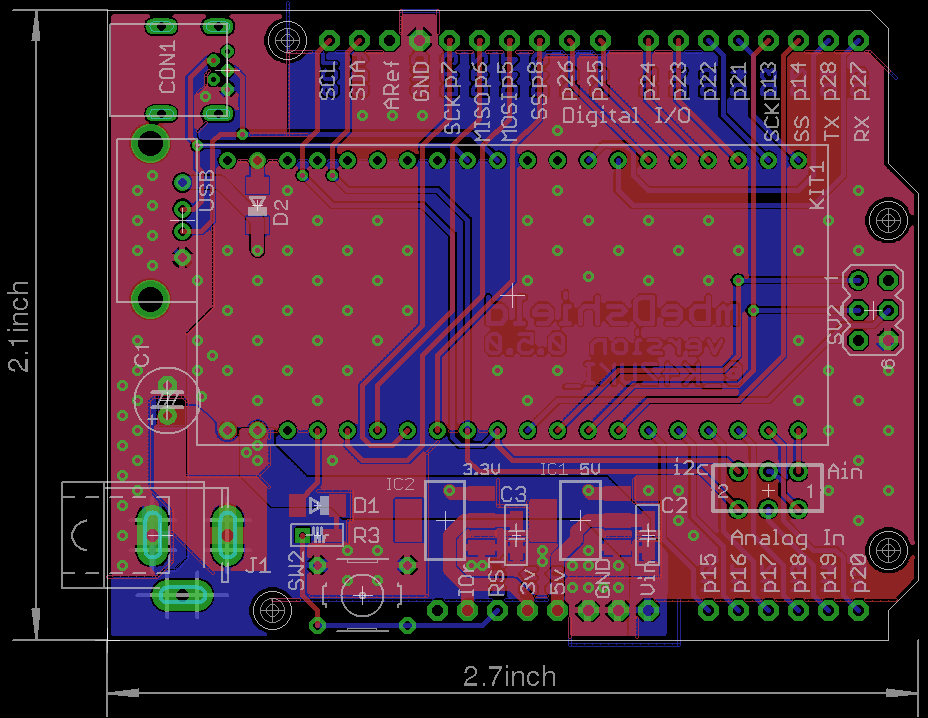
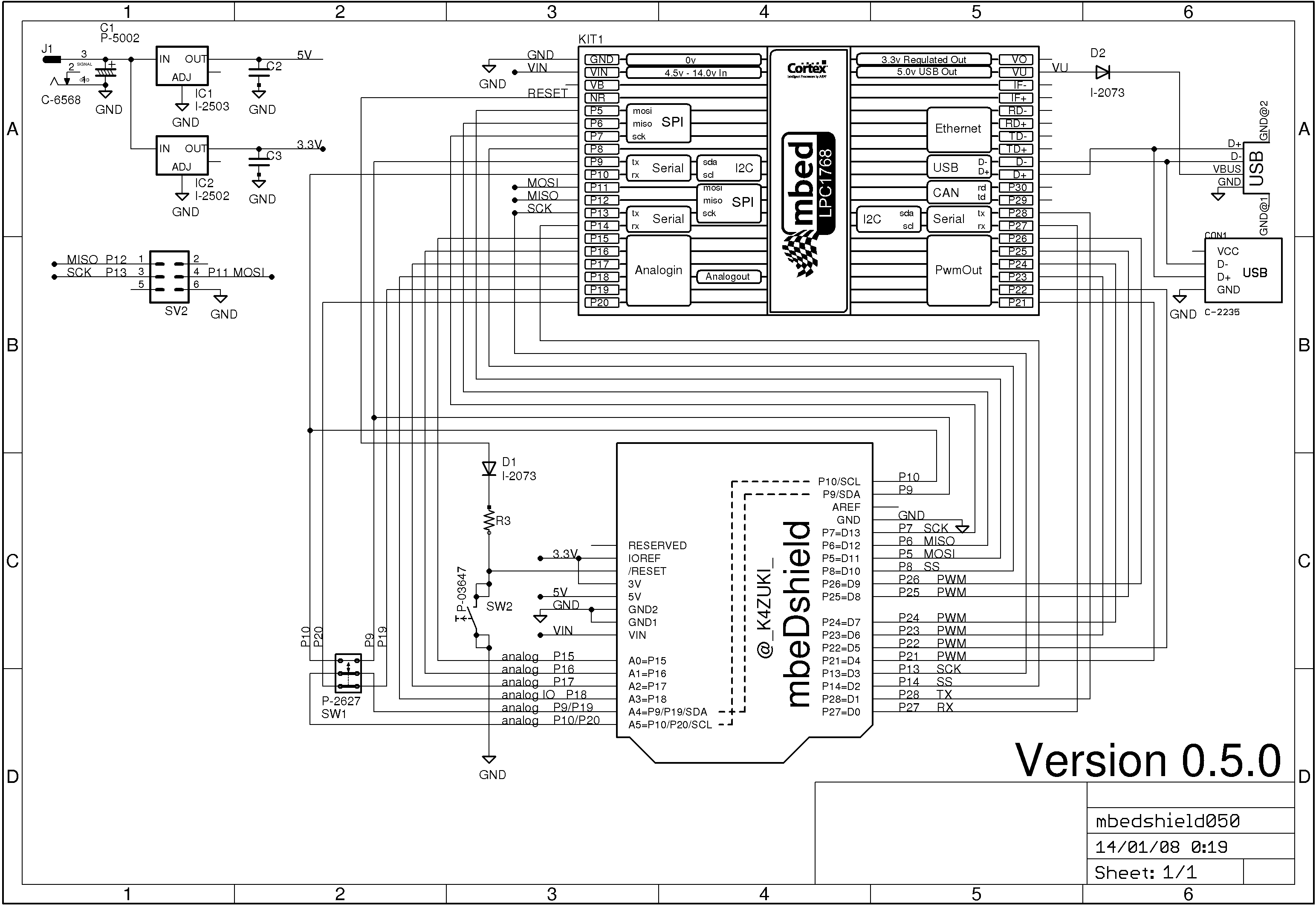
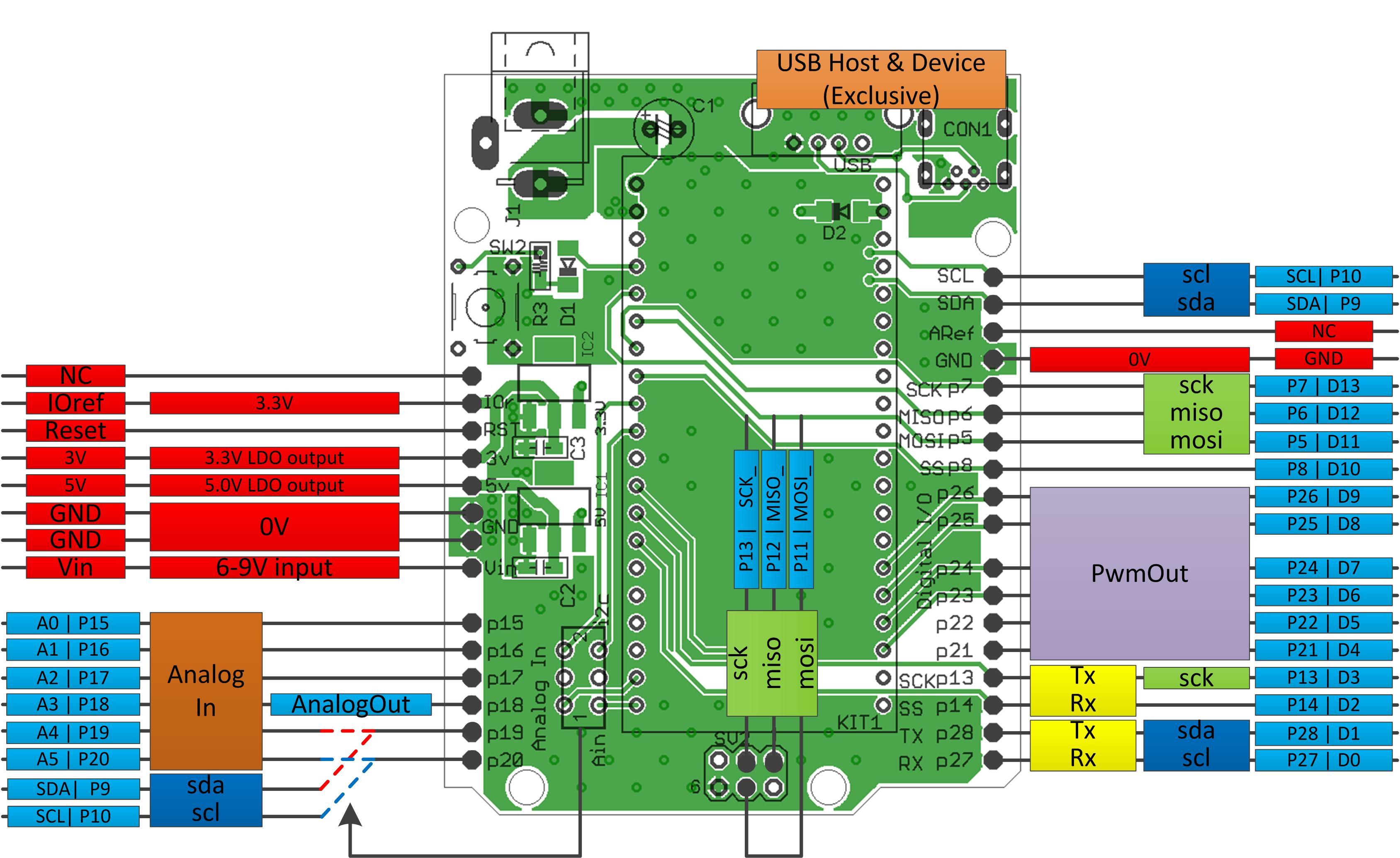
Photos
- Board photo vvv
- Schematic photo vvv
- Functionality photo vvv
Latest eagle files
PCB >> /media/uploads/k4zuki/mbedshield050.brd
SCH >> /media/uploads/k4zuki/mbedshield050.sch
BIG changes from previous version
- Ethernet RJ45 connector is removed.
- http://mbed.org/components/Seeed-Ethernet-Shield-V20/ is the biggest hint to use Ethernet!
MostALL of components can be bought at Akizuki http://akizukidenshi.com/- But sorry, they do not send parts to abroad
- Pinout is changed!
| arduino | 0.4.0 | 0.5.0 |
|---|---|---|
| D4 | p12 | p21 |
| D5 | p11 | p22 |
| MOSI_ | none | p11 |
| MISO_ | none | p12 |
| SCK_ | none | p13 |
This design has bug(s)
- I2C functional pin differs between 1768 and 11U24.
Fixed bugs here
- MiniUSB cable cannot be connected on mbed if you solder high-height electrolytic capacitor on C3.
- http://akizukidenshi.com/catalog/g/gP-05002/ is the solution to make this 100% AKIZUKI parts!
- the 6-pin ISP port is not inprimented in version 0.4.0
it will be fixed in later version 0.4.1/0.4.2/0.5.0This has beenfixed
I am doing some porting to use existing arduino shields but it may faster if you do it by yourself...
you can use arduino PinName "A0-A5,D0-D13" plus backside SPI port for easier porting.
To do this you have to edit PinName enum in
- "mbed/TARGET_LPC1768/PinNames.h" or
- "mbed/TARGET_LPC11U24/PinNames.h" as per your target mbed.
here is the actual list: This list includes define switch to switch pin assignment
part_of_PinNames.h
USBTX = P0_2,
USBRX = P0_3,
//from here mbeDshield mod
D0=p27,
D1=p28,
D2=p14,
D3=p13,
#ifdef MBEDSHIELD_050
MOSI_=p11,
MISO_=p12,
SCK_=p13,
D4=p21,
D5=p22,
#else
D4=p12,
D5=p11,
#endif
D6=p23,
D7=p24,
D8=p25,
D9=p26,
D10=p8,
D11=p5,
D12=p6,
D13=p7,
A0=p15,
A1=p16,
A2=p17,
A3=p18,
A4=p19,
A5=p20,
SDA=p9,
SCL=p10,
//mbeDshield mod ends here
// Not connected
NC = (int)0xFFFFFFFF
I2CSlave.h
- Committer:
- k4zuki
- Date:
- 2014-05-06
- Revision:
- 72:e0dca162df14
- Parent:
- 65:5798e58a58b1
File content as of revision 72:e0dca162df14:
/* mbed Microcontroller Library
* Copyright (c) 2006-2013 ARM Limited
*
* Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
* you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
* You may obtain a copy of the License at
*
* http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
*
* Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
* distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
* WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
* See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
* limitations under the License.
*/
#ifndef MBED_I2C_SLAVE_H
#define MBED_I2C_SLAVE_H
#include "platform.h"
#if DEVICE_I2CSLAVE
#include "i2c_api.h"
namespace mbed {
/** An I2C Slave, used for communicating with an I2C Master device
*
* Example:
* @code
* // Simple I2C responder
* #include <mbed.h>
*
* I2CSlave slave(p9, p10);
*
* int main() {
* char buf[10];
* char msg[] = "Slave!";
*
* slave.address(0xA0);
* while (1) {
* int i = slave.receive();
* switch (i) {
* case I2CSlave::ReadAddressed:
* slave.write(msg, strlen(msg) + 1); // Includes null char
* break;
* case I2CSlave::WriteGeneral:
* slave.read(buf, 10);
* printf("Read G: %s\n", buf);
* break;
* case I2CSlave::WriteAddressed:
* slave.read(buf, 10);
* printf("Read A: %s\n", buf);
* break;
* }
* for(int i = 0; i < 10; i++) buf[i] = 0; // Clear buffer
* }
* }
* @endcode
*/
class I2CSlave {
public:
enum RxStatus {
NoData = 0,
ReadAddressed = 1,
WriteGeneral = 2,
WriteAddressed = 3
};
/** Create an I2C Slave interface, connected to the specified pins.
*
* @param sda I2C data line pin
* @param scl I2C clock line pin
*/
I2CSlave(PinName sda, PinName scl);
/** Set the frequency of the I2C interface
*
* @param hz The bus frequency in hertz
*/
void frequency(int hz);
/** Checks to see if this I2C Slave has been addressed.
*
* @returns
* A status indicating if the device has been addressed, and how
* - NoData - the slave has not been addressed
* - ReadAddressed - the master has requested a read from this slave
* - WriteAddressed - the master is writing to this slave
* - WriteGeneral - the master is writing to all slave
*/
int receive(void);
/** Read from an I2C master.
*
* @param data pointer to the byte array to read data in to
* @param length maximum number of bytes to read
*
* @returns
* 0 on success,
* non-0 otherwise
*/
int read(char *data, int length);
/** Read a single byte from an I2C master.
*
* @returns
* the byte read
*/
int read(void);
/** Write to an I2C master.
*
* @param data pointer to the byte array to be transmitted
* @param length the number of bytes to transmite
*
* @returns
* 0 on success,
* non-0 otherwise
*/
int write(const char *data, int length);
/** Write a single byte to an I2C master.
*
* @data the byte to write
*
* @returns
* '1' if an ACK was received,
* '0' otherwise
*/
int write(int data);
/** Sets the I2C slave address.
*
* @param address The address to set for the slave (ignoring the least
* signifcant bit). If set to 0, the slave will only respond to the
* general call address.
*/
void address(int address);
/** Reset the I2C slave back into the known ready receiving state.
*/
void stop(void);
protected:
i2c_t _i2c;
};
} // namespace mbed
#endif
#endif
