You are viewing an older revision! See the latest version
USBMSD
The USBMSD interface is used to emulate a mass storage device over USB. You can use this class to store or load data to and from a storage chip (SDcard, flash,...). This class implements the MSD protocol and calls pure virtual functions such as disk_initialize, disk_write or disk_read to interact with a storage chip. More information on how to use this class with your own chip can be found at the end of this document.
The USB connector should be attached to p31 (D+), p32 (D-) and GND. You can also connect the USB power to VIN to power the mbed when connected.
Hello World! with an SD card¶
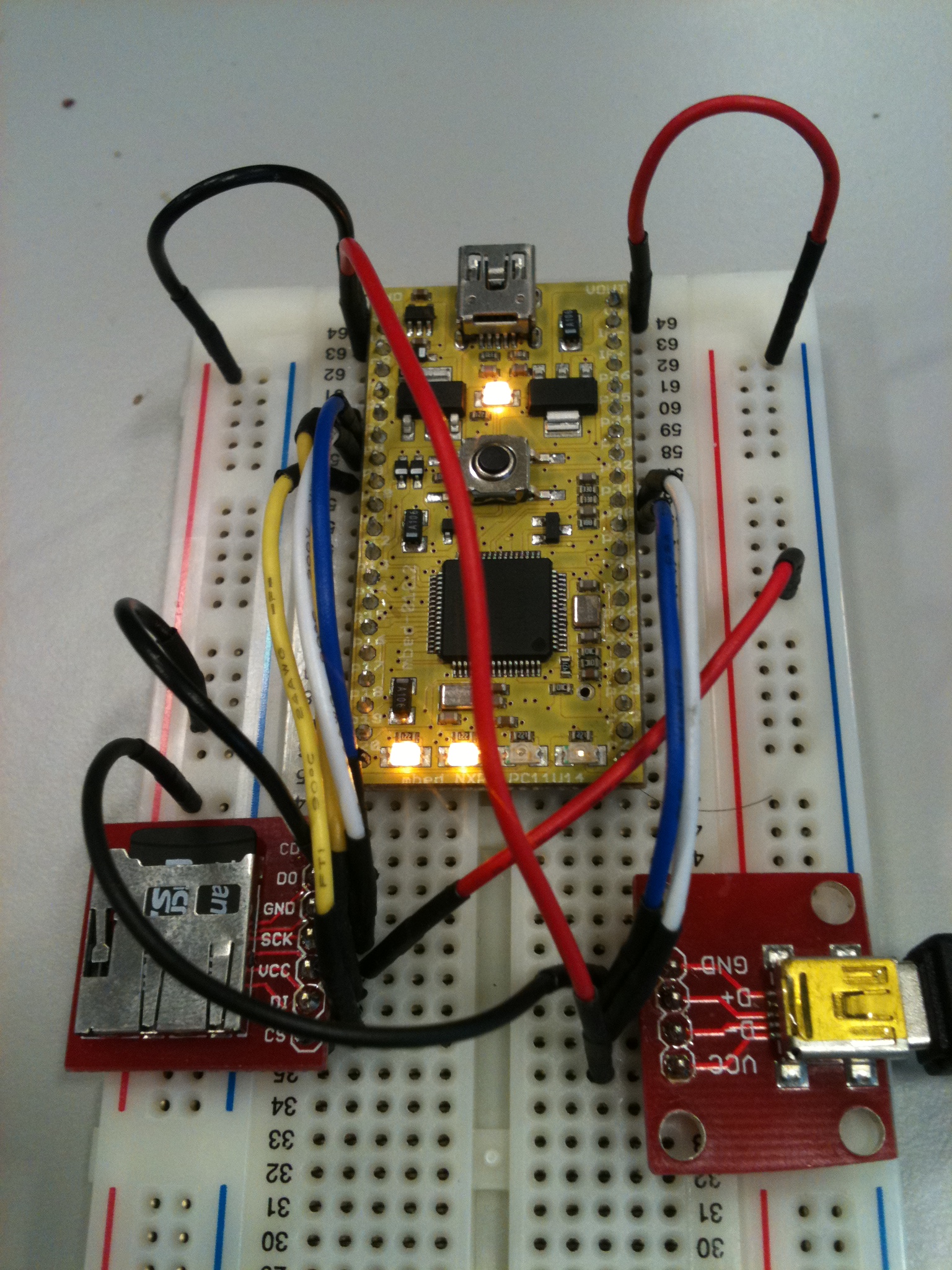
The following program has been tested with a micro SD card(Transcend micro SD 1GB).
Hello World! with an SD card
#include "mbed.h"
#include "USBMSD_SD.h"
USBMSD_SD sd(p5, p6, p7, p8);
int main() {
while(1);
}
Import programUSBMSD_SD_HelloWorld_Mbed
USBMSD SD card Hello World for Mbed platforms
API¶
How to use USBMSD with your own chip ?¶
The USBMSD class implements the MSD protocol. It permits to access a memory chip (flash, sdcard,...) from a computer over USB. But this class doesn't work standalone, you need to subclass this class and define pure virtual functions which are called in USBMSD.
You have to inherit from USBMSD and define ALL the following pure virtual functions:
- virtual int disk_read(char * data, int block): function to read a block
- virtual int disk_write(const char * data, int block): function to write a block
- virtual int disk_initialize(): function to initialize the memory
- virtual int disk_sectors(): return the number of blocks
- virtual int disk_size(): return the memory size
- virtual int disk_status(): return the status of the storage chip (0: OK, 1: not initialized, 2: no medium in the drive, 4: write protection)
All functions names are compatible with the fat filesystem library. So you can imagine using your own class with USBMSD and the fat filesystem library in the same program. Just be careful because there are two different parts which will access the sd card. You can do a master/slave system using disk_status().
Once these functions defined, you can call connect() (at the end of the constructor of your class for instance) of USBMSD to connect your mass storage device. connect() will first call disk_status() to test the status of the disk. If disk_status() returns 1 (disk not initialized), then disk_initialize() is called. After this step, connect() will collect information such as the number of blocks and the memory size.
A class example which inherits from USBMSD has been developed in order to access an SD card. You can follow this example and write your own class to access your storage chip.
Import libraryUSBMSD_SD
USBMSD example using an SD card
