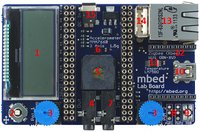
mbed Application Board
Application board for mbed NXP LPC1768
Hello World
Import programapp-board-LCD
Example program printing text to the LCD on the mbed application board
Library
Import libraryC12832
C12832 LCD with generic interface
Notes
The new application board has been designed to enable the maximum number of potential experiments and projects, with the minimum footprint.
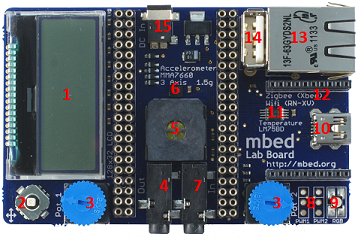 | 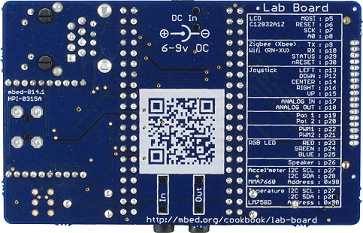 |
Although that there are 2x20 way headers for the mbed for jumper wiring pins off-board, it's a fairly well encapsulated platform.
Where to buy
Feature list
- 128x32 Graphics LCD
- 5 way joystick
- 2 x Potentiometers
- 3.5mm Audio jack (Analog Out)
- Speaker, PWM connected
- 3 Axis +/1 1.5g Accelerometer
- 3.5mm Audio jack (Analog In)
- 2 x Servo motor headers
- RGB LED, PWM connected
- USB-mini-B Connector
- Temperature sensor
- Socket for for Xbee (Zigbee) or RN-XV (Wifi)
- RJ45 Ethernet Connector
- USB-A Connector
- 1.3mm DC Jack input
1. 128x32 LCD
An example program to print text and variables to the LCD
Import program
00001 #include "mbed.h" 00002 #include "C12832.h" 00003 00004 00005 C12832 lcd(p5, p7, p6, p8, p11); 00006 00007 int main() 00008 { 00009 int j=0; 00010 lcd.cls(); 00011 lcd.locate(0,3); 00012 lcd.printf("mbed application board!"); 00013 00014 while(true) { // this is the third thread 00015 lcd.locate(0,15); 00016 lcd.printf("Counting : %d",j); 00017 j++; 00018 wait(1.0); 00019 } 00020 }
Import libraryC12832
C12832 LCD with generic interface
A full featured test program :
Import programlab1
test program for mbed Lab Board
Demo for using bitmap graphic :
Import programChristmas-LCD
Demo for using bitmap graphic
2. Joystick
An example program for the mbed application board that uses the joystick button. LED1,2,3,4 light in sequence with up, down, left, right, and pushing the button lights them all (as a 80's computer gamer, I want to call this "fire!")
Note: that the orientation is looking at the screen in landscape, with the row of connectors at the bottom
Import programkill_the_bit
Classic Kill the Bit game for the application board. Press joystick down to kill off the leftmost LED, but if your timing is off more LEDs turn on. LEDs flash and speaker beeps when all LEDs are off.
3. 2 x Potentiometers
To be completed
4. Analog Out
Plug in a pair of earphones.
Play music from a *.wav audio file on PC speakers. See Application Board Waveplayer Demo for complete instructions.
Import programAppBoard_Waveplayer
A wave player demo setup for the mbed application board. Reads a wave file from a USB flash drive, and outputs to the onboard speaker (very low volume) and the analog audio out jack that can be connected to a set of PC speakers for more volume. A wave file for the demo is available at http://mbed.org/media/uploads/4180_1/sample.wav. Copy it to the USB drive. See http://mbed.org/users/4180_1/notebook/application-board-waveplayer-demo/ for more details and instructions.
5. Speaker
A frequency sweep. Press the fire button to to play it again!
Play music from a *.wav audio file on the speaker. See Application Board Waveplayer Demo for complete instructions.
Import programAppBoard_Waveplayer
A wave player demo setup for the mbed application board. Reads a wave file from a USB flash drive, and outputs to the onboard speaker (very low volume) and the analog audio out jack that can be connected to a set of PC speakers for more volume. A wave file for the demo is available at http://mbed.org/media/uploads/4180_1/sample.wav. Copy it to the USB drive. See http://mbed.org/users/4180_1/notebook/application-board-waveplayer-demo/ for more details and instructions.
6. 3 Axis Accelerometer
Import program
00001 //Uses the measured z-acceleration to drive leds 2 and 3 of the mbed 00002 00003 #include "mbed.h" 00004 #include "MMA7660.h" 00005 00006 MMA7660 MMA(p28, p27); 00007 00008 DigitalOut connectionLed(LED1); 00009 PwmOut Zaxis_p(LED2); 00010 PwmOut Zaxis_n(LED3); 00011 00012 int main() { 00013 if (MMA.testConnection()) 00014 connectionLed = 1; 00015 00016 while(1) { 00017 Zaxis_p = MMA.z(); 00018 Zaxis_n = -MMA.z(); 00019 } 00020 00021 }
Import libraryMMA7660
Library for the MMA7660 triple axis accelerometer
Import programapp-board-Bubble-Level
This demo uses the application board’s three axis accelerometer and the LCD display working in graphics mode to build an electronic version of a bubble level.
7. Analog In
To be completed
8. Servo Motor
An example program that uses the two potentiometers to set the position of the servo motors. You'll need to supply 6v into the DC socket, (1.3mm, center/tip positive)
Import libraryServo
A class to control a model R/C servo, using a PwmOut
9. RGB LED
An example program that cycles the on board RGB LED through various colours.
Information
The RGB LED is common anode, so that "0" is on, and "1" is off. For PWM, the closer to 0.0 the brighter, the closer to 1.0 the dimmer. use (1.0 - value) to invert.
Import program
00001 #include "mbed.h" 00002 00003 PwmOut r (p23); 00004 PwmOut g (p24); 00005 PwmOut b (p25); 00006 00007 int main() 00008 { 00009 r.period(0.001); 00010 while(1) { 00011 for(float i = 0.0; i < 1.0 ; i += 0.001) { 00012 float p = 3 * i; 00013 r = 1.0 - ((p < 1.0) ? 1.0 - p : (p > 2.0) ? p - 2.0 : 0.0); 00014 g = 1.0 - ((p < 1.0) ? p : (p > 2.0) ? 0.0 : 2.0 - p); 00015 b = 1.0 - ((p < 1.0) ? 0.0 : (p > 2.0) ? 3.0 - p : p - 1.0); ; 00016 wait (0.01); 00017 } 00018 } 00019 }
Import programapp-board-RGB2
Example program to cycle the RGB LED on the mbed application board through all colours
10. USB Device
Import program
00001 #include "mbed.h" 00002 #include "USBMouse.h" 00003 00004 USBMouse mouse; 00005 00006 int main() { 00007 int16_t x = 0; 00008 int16_t y = 0; 00009 int32_t radius = 10; 00010 int32_t angle = 0; 00011 00012 while (1) { 00013 x = cos((double)angle*3.14/180.0)*radius; 00014 y = sin((double)angle*3.14/180.0)*radius; 00015 00016 mouse.move(x, y); 00017 angle += 3; 00018 wait(0.001); 00019 } 00020 }
Import programUSBKeyboard_HelloWorld
USBKeyboard Hello World
Import programUSBSerial_HelloWorld
USBSerial Hello World
Import programUSBHID_HelloWorld
USBHID Hello World
11. LM75B Temperature sensor
An example program to read the current temperature from the LM75B and display it on the LCD
Import program
00001 #include "mbed.h" 00002 #include "LM75B.h" 00003 #include "C12832.h" 00004 00005 C12832 lcd(p5, p7, p6, p8, p11); 00006 00007 LM75B sensor(p28,p27); 00008 Serial pc(USBTX,USBRX); 00009 00010 int main () 00011 { 00012 00013 //Try to open the LM75B 00014 if (sensor.open()) { 00015 printf("Device detected!\n"); 00016 00017 while (1) { 00018 lcd.cls(); 00019 lcd.locate(0,3); 00020 lcd.printf("Temp = %.3f\n", (float)sensor); 00021 wait(1.0); 00022 } 00023 00024 } else { 00025 error("Device not detected!\n"); 00026 } 00027 00028 }
Import libraryLM75B
A simply library for the LM75B I2C temperature sensor
12. Xbee socket
Websocket over Wifly - Hello World - This example send messages to the mbed websocker server over a wifi connection using the RN-XV Wifly module.
The output can be seen at
Import program
00001 #include "mbed.h" 00002 #include "WiflyInterface.h" 00003 #include "Websocket.h" 00004 #include "LM75B.h" 00005 #include "MMA7660.h" 00006 00007 00008 /* wifly interface: 00009 * - p9 and p10 are for the serial communication 00010 * - p30 is for the reset pin 00011 * - p29 is for the connection status 00012 * - "mbed" is the ssid of the network 00013 * - "password" is the password 00014 * - WPA is the security 00015 */ 00016 00017 WiflyInterface wifly(p9, p10, p30, p29, "mbed", "password", WPA); 00018 00019 // accelerometer 00020 MMA7660 acc(p28, p27); 00021 00022 // temperature sensor 00023 LM75B tmp(p28,p27); 00024 00025 00026 int main() 00027 { 00028 char json_str[100]; 00029 00030 wifly.init(); //Use DHCP 00031 while (!wifly.connect()); 00032 printf("IP Address is %s\n\r", wifly.getIPAddress()); 00033 00034 // See the output on http://sockets.mbed.org/app-board/viewer 00035 Websocket ws("ws://sockets.mbed.org:443/ws/app-board/wo"); 00036 00037 // connect WS server 00038 while (!ws.connect()); 00039 00040 while (1) { 00041 // create json string with acc/tmp data 00042 sprintf(json_str, "{\"id\":\"app_board_wifly_EW2013\",\"ax\":%d,\"ay\":%d,\"az\":%d, \"tmp\":%d}", (int)(acc.x()*360), (int)(acc.y()*360), (int)(acc.z()*360), (int)tmp.read()); 00043 00044 // send str 00045 ws.send(json_str); 00046 00047 wait(0.1); 00048 } 00049 }
HTTP Client over Wifly - Hello World
Import programapp-board-Wifly-HTTPClient
An example program using the HTTP Client over wifly, creat
13. Ethernet Interface
NTP Hello World - This example fetches the the time using NTP, and prints it over the USB Serial interface. Be sure to have been through /handbook/SerialPC to make sure you have a serial console
Import programNTPClient_HelloWorld
Simple example demonstrating how to use the NTP Client to set the time
HTTP Client Hello World
Import programHTTPClient_HelloWorld
Simple example demonstrating how to use GET & POST requests with the HTTP Client
Websocket Accelerometer-Temperature demo - This example streams acceleration and temperature data to a websocket server. Visit app-board viewer to have a real time feed.
Import programapp-board-Ethernet-Websocket
Modifed version from Samuel Mokrani Changed URL to push data to sensor page Added visualisation page URL as a comment
WiFly-xively-jumpstart-demo - Xively Jumpstart demo with WiFly module.
Import programWiFly-xively-jumpstart-demo
Xively Jumpstart Demo with WiFly module
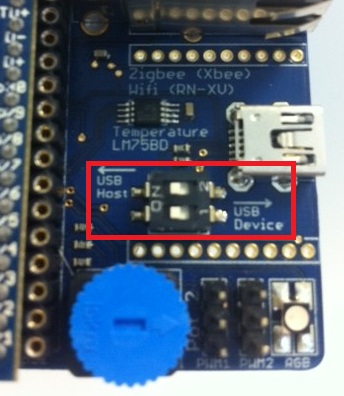
14. USB Host
Important!
When using the mbed as a USB host, 15k Ohm pull down resistors are needed on the D+ and D- signals, as per the USB specification. This can be achieved by switching both switches the DIP switch to the "USB Host" position
Flash disk Hello World This example program writes the file "test.csv" to a USB flash stick, taking 100 samples (20 per second for 5 seconds) from pot1. The resulting CSV file can easily be plotted as a graph in Excel!
Import program
00001 #include "mbed.h" 00002 #include "MSCFileSystem.h" 00003 00004 MSCFileSystem fs("fs"); 00005 DigitalOut led(LED1); 00006 AnalogIn pot1(p19); 00007 00008 int main() 00009 { 00010 FILE *fp = fopen("/fs/test.csv","w"); 00011 printf("Create filehandle for test.csv\n"); 00012 00013 printf("Writing to file\n"); 00014 for (int i=0; i<100; i++) { 00015 fprintf(fp,"%.2f\n",pot1.read()); 00016 wait(0.05); 00017 led=!led; 00018 } 00019 00020 fclose(fp); 00021 printf("Close the handle\n"); 00022 led=1; 00023 }
Details
| Form factor | 55mm x 86mm x 19mm (with mbed) |
| 128x32 Graphics LCD, SPI Interface | Newhaven C12832A1Z MOSI:p5 nRESET:p6 SCK:p7 A0:p8 |
| 3 Axis +/1 1.5g Accelerometer,I2C Interface | Freescale MMA7660 SCL:p27 SDA:p28 Address:0x98 |
| Temperature sensor | LM75B SCL:p27 SDA:p28 Address:0x90 |
| 5 way Joystick | ALPS SKRHADE010 Down:p12 Left:p13 Centre:p14 Up:p15 Right:p16 |
| 2 x Potentiometers | Iskra PNZ10ZA, 10k Pot 1 (left) :p19 Pot 2 (right):p20 |
| 2 x 3.5mm Audio jack (Analog In/Out) | CUI Inc SJ-3523-SMT Analog In:p17 Analog Out:p18 |
| 2 x Servo motor headers | PWM1:p22 PWM2:p21 |
| RGB LED, PWM connected | Cree Inc CLV1A-FKB Red:p23 Green:p24 Blue:p25 |
| Speaker, PWM Connected | MULTICOMP MCSMT-8030B-3717 p26 |
| USB-B Connector | Neltron, 5075ABMR-05-SM1 |
| USB-A Connector | MULTICOMP,USB-A-V |
| RJ45 Ethernet conenctor | Pulse Jack, J00-0045NL |
| 1.3mm DC Jack input | CLIFF, FC68145S 1.3mm 6v-9v Centre positive |
Schematics
You need to log in to post a discussion